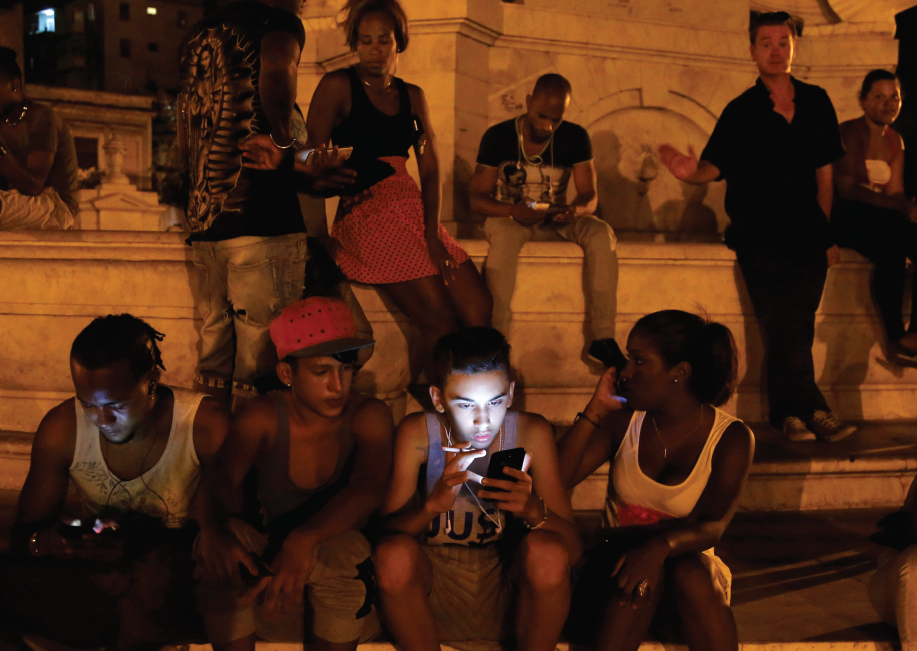Published in Current History, February 2015, here: INTERNAL EMBARGO
See original essay here: Overcoming Cuba’s Internal Embargo
By Ted A. Henken and Archibald R.M. Ritter
In scores of interviews conducted over the past 15 years with Cuban entrepreneurs for our new book, “Entrepreneurial Cuba,” Arch Ritter and I often heard the following two very pregnant Cuban sayings:
“El ojo del amo engorda el caballo” (The eye of the owner fattens the horse) and “El que tenga tienda que la atienda, o si no que la venda” (Whoever has a store should tend to it, and if not then sell it”).
The first adage indicates that the quality of a good or service improves when the person performing it enjoys autonomy and has a financial stake in the outcome. The second saying suggests that if the Cuban government is unable to “tend its own stores,” then it should let others take them over.
In essence, this popular wisdom demands that the state turn over to the private sector the economic activities it cannot operate effectively itself—many of which are already widely practiced in Cuba’s ubiquitous underground economy.
In other words, the U.S. embargo – recently dealt a near fatal blow by the joint decision by Presidents Barack Obama and Raúl Castro to reestablish diplomatic relations after almost 54 years – is hardly the principal “blockade” standing in the way of Cuba’s economic revitalization. Though the American “bloqueo” has long been the target of withering and well-deserved international condemnation, on the island Cubans themselves are much more likely to criticize what they bitterly refer to as the “auto-bloqueo” (internal embargo) imposed by the Cuban government itself on the entrepreneurial ingenuity, access to uncensored information and open communications, as well as basic civil and political rights of the Cuban people.
President Barack Obama has opened a door to potential U.S. investment in (and import/export to and from) Cuba’s entrepreneurial and telecom sectors. But is Raúl Castro willing to allow U.S. companies to operate on the island? More important still, is his government ready to open up to the Cuban people by beginning to relinquish its tight control over private enterprise and the Internet?
While we believe that it is both good and necessary for the United States to open up to Cuba and vice versa (to paraphrase the late Pope John Paul II), our book argues that little economic progress or political freedom will be enjoyed by Cubans themselves until the Cuban government opens up to its own people, ceases to demand their acquiescence as subjects, and begins to respect them as citizens, consumers, and entrepreneurs with defensible and inalienable economic and political rights of their own.
In fact, two weeks following the historic mid-December Obama-Castro announcement, the Cuban government received its first public test of whether its internal embargo would now be relaxed in light of the sea-change in U.S. policy. On December 30, the internationally renown Cuban artist Tania Bruguera organized a public act of performance art in Havana’s iconic Revolutionary Plaza. Dubbed “#YoTambienExijo,” Bruguera invited Cuban citizens to “share their own demands” on the government and visions for the island’s future for one minute each at an open-mic set up in the Plaza. Predictably, the government responded by arresting and detaining scores of artists, activists, and independent journalists, which amounted to an even more public “performance” of its own typically repressive tactics, as news of the event echoed in the international media on the final day of the year.
Thus, while we can celebrate the fact that the U.S. and Cuban governments have finally agreed to begin respectful, diplomatic engagement, the Cuban government’s failure to respectfully engage with the diverse and often dissenting voices of its own citizens makes us wonder with Bruguera whether “it’s the Cuban people who will benefit from this new historic moment,” as she put it in her previously circulated open letter to Raúl Castro.
Between 1996 and 2006, President Fidel Castro pursued an economic policy retrenchment that gradually phased out the pro-market reforms of the early 1990s, indicating that he was more aware of the political risks that popular entrepreneurship would pose to his centralized political control than of the economic benefits it could provide. Therefore, he was unwilling to transfer more than a token portion of the state “store” to private entrepreneurs.
His brother, Raúl Castro, whose presidency began in 2006, has significantly eased this resistance. While the underlying goal of economic reform is still to “preserve and perfect socialism,” he has started to deliberatively shrink the state “store” and transfer the production of many goods and services to the more than half-a-million new small enterprises, including both private and cooperative ventures.
However, much more remains to be done in reforming policies toward microenterprise so that it can contribute fully to productive employment, innovation, and economic growth. For example, 70 percent of the newly self-employed were previously unemployed, meaning that they likely converted previously existing underground enterprises into legal ones, doing little to absorb the 1.8 million workers slated for state-sector layoffs. Moreover, only 7 percent of self-employed are university graduates, and most of them work in “low tech” activities because almost all professional self-employment is prohibited. This acts a “blockade” on the effective use of Cuba’s well-educated labor force, obstructing innovation and productivity.
A further goal of the tentative reforms to date has been to facilitate the emergence of cooperative and small enterprise sectors so that they can generate sustained improvements in material standards of living. This can only be achieved with additional reforms that effectively “end the embargo” against Cuban entrepreneurs.
Among the necessary changes would be:
1. Opening the professions to private enterprise,
2. Implementing affordable wholesale markets,
3. Providing access to foreign exchange and imports (a fiercely guarded state monopoly),
4. Establishing effective credit facilities,
5. Permitting the establishment of retailing enterprises, and
6. Relaxing the tax burden on small enterprise, which now discriminates against domestic enterprise in favor of foreign investors.
Progress in all these areas would be greatly facilitated by access to U.S. investors and markets (both as a source of desperately needed wholesale inputs and as a place to sell their products), something now possible following the implementation of Obama’s historic policy changes during the coming year.
However, it remains to be seen whether Raúl has the political will to intensify the internal reform process. The outright prohibition of activities the government prefers to keep under state monopoly allows it to exercise control over Cuban citizens and impose an apparent order over society. However, this comes at the cost of pushing all targeted economic activity (along with potential tax revenue) back into the black market – where much of it lurked prior to 2010.
On the other hand, the inclusion and regulation of the many private activities dreamed up and market-tested by Cuba’s always inventive entrepreneurial sector would create more jobs, a higher quality and variety of goods and services at lower prices, while also increasing tax revenue. However, these benefits come at the political cost of allowing greater citizen autonomy, wealth and property in private hands, and open competition against state monopolies.
The viability of Cuba’s reforms also depends on the recently announced changes in U.S. policy toward Cuba and on Cuba’s changing policy toward its émigrés, who already play a major role in the Cuban economy as suppliers of start-up capital via the billions of dollars they provide annually in remittances. Such investment could be expanded if the Cuban government were to deepen its recent migration reforms by granting greater economic rights to its extensive émigré community.
Obama’s relaxation of U.S. policy will inevitably shift the political calculus that underlies economic reform on the island. As external obstacles to Cuba’s economic revitalization are removed, the onus will fall with increased pressure on the Cuban government to broaden and deepen its initial reforms, since it alone will be to blame for poor performance.
For example, organizations like Catholic Church-affiliated CubaEmprende have already begun to offer entrepreneurship workshops to small business owners with the financial backing of Cuban-Americans. Now that they needn’t worry about the threat of U.S. sanctions, will this and other similar projects be provided the legal and institutional space to flourish by the Cuban government?
Despite a continued state monopoly on the mass media and one of the Western Hemisphere’s lowest Internet penetration rates, in recent years Cuba has seen a number of significant developments in information and communication technology (ICT) capabilities, access to uncensored news, and the availability of new dissemination channels for digital data.
These developments include:
1. The spread of the worldwide blogging and citizen journalism phenomena to Cuba;
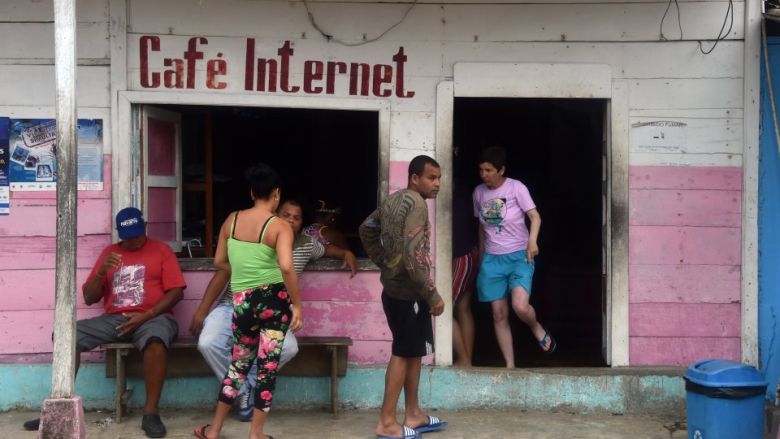
2. The connection of a fiber-optic Internet cable to the island from Venezuela in 2013, followed by the opening of 118 Internet cafés in June 2013 and access to e-mail via cell phone for the first time in 2014;
3. The appearance of a small number of independent, island-based news outlets – including the news and opinion websites Havana Times, On Cuba, and 14ymedio (launched by pioneering blogger Yoani Sánchez in May 2014);
4. The creation of a number of unauthorized “mesh” networks that use private Wi-Fi networks to communicate and share information, and
5. The emergence of an underground digital data distribution system known as “el paquete” (the packet).
Each of these developments could be accelerated by the new U.S. policy that allows American telecom providers to do business in Cuba, but only if the Cuban government is willing to allow diversification and freer competition in its centralized, monopolistic ICT system.
For example, the so-called “packet” phenomenon currently acts as an alternate, off-line Internet on the island making huge amounts of electronic data (CDs, DVDs, video games, books, “apps,” computer programs, news, and so forth) readily available for purchase in Cuba’s digital “black market.” While much data continues to circulate via thumb-drives, there is also a market for entire external hard drives of data bought and sold not in megabytes or gigabytes, but in terabytes – and all outside the rigid control of the state media production and distribution system – amounting to an indirect but very serious and effective challenge to the so-called “política cultural de la Revolución.”
This digital black market arises from the fact that many products—especially the latest electronic gadgets—are either priced far out of reach for most Cubans in “las tiendas estatales,” not sold at all, or even banned outright. More recently, the small but rapidly growing number of Cubans who have joined the smart phone revolution (often purchasing their Androids or iPhones via the blocked site Revolico.com, a Cuban version of Craig’s List) have benefitted from the proliferation of “apps” especially configured for Cuba’s peculiar off-line environment.
Undoubtedly, such a peculiar digital media environment will be fundamentally transformed if American data, service, and hardware providers were given access to the Cuban market. At the very least, prices are bound to fall, speed increase, and access expand, with the quality and quantity of digital ICT equipment improving.
A key recent development was the June 2014 trip of top Google executives to the island, including company co-founder Eric Schmidt, with the purpose of “promoting a free and open Internet.” To that end, they met both with leading cyber-activist Yoani Sánchez and government officials, while also interacting with students at Cuba’s University of Computer Science. Upon returning to the U.S., Schmidt declared that Cuba was trapped in the Internet of the 1990s and heavily censored, with American-engineered hardware and software losing out to Chinese ICT infrastructure.
He also reasoned that the U.S. embargo “makes absolutely no sense” if Washington’s aim is to open the island up to the freer flow of information. “If you wish the country to modernize,” Schmidt argued, “the best way to do this is to empower the citizens with smart phones and encourage freedom of expression and put information tools into the hands of Cubans directly.”
The greatly expanded telecom opportunities for U.S. companies and the decision to review the designation of Cuba as a state sponsor of terrorism, both included in December’s announcement to normalize relations, indicate that the Obama administration was convinced by Schmidt’s logic.
The slow pace and (so far) only marginally successful results of Cuba’s economic reforms to date has put the Cuban government under rising internal pressure to expand Internet services and from abroad to meet the needs of the new foreign investors it hopes to attract. This eventuality – now with the help of U.S. investment and technology – could positively impact the population’s access to the web.
At the same time, the government is clearly looking to the Chinese example as it contemplates ramping up its own Internet capabilities, hoping to remake the web in its authoritarian image and forestall any of its democratizing impacts.
Still, in the months following the Google visit, the company announced that it was unblocking island access to its free cloud-based Chrome search engine as well as popular applications such as Google Play and Google Analytics – a decision that could not have been made without tacit approval from the Obama administration. Events in 2015 will reveal how much further the Cuban government is willing to allow Google and other Internet and telecom companies to go.
While these digital developments are significant, it remains difficult to determine to what extent they will affect ordinary Cubans, given that the government itself estimates the Internet access rate at an extremely low 26 percent. Even this figure conflates access to the Internet with the island’s limited internal “intranet,” and counts sporadic access to e-mail in the same category as full access to the World Wide Web.
Moreover, while 118 new cyber-cafes opened across the island in June 2013, the service is a state monopoly available only to those able to pay in hard currency. Full access for one hour costs the equivalent of the average weekly salary. Thus, expanded access to ICT in Cuba takes place in a context of a connectivity that can be described as slow, expensive, and censored, with certain sites – such as 14ymedio – blocked outright.
Devices such as computers, tablets, and smartphones are scarce and costly; the purchase and importation of key equipment such as routers and other Wi-Fi technology are highly controlled. Indeed, it is still not legally possible for the vast majority of Cuban citizens to obtain a household Internet connection, and there is virtually no legal access on the island to wireless networks and fully functional mobile technology or smart phones with data plans, outside of international hotels and certain government institutions, and select educational facilities.
The government has recognized these limitations and made commitments to remedy them, but there is no clear timeline or way to hold the government or its telecom monopoly Etecsa accountable to citizens, consumers, or Cuba’s emerging class of private entrepreneurs.
Cuban citizens of all stripes are working to overcome the substantial obstacles to entrepreneurship and free expression. This effort, however, takes place in an asphyxiating climate of political polarization, where Cubans have been doubly blockaded by the U.S. embargo on one side and by the ongoing internal embargo on the other.
This is why the recent growth of domestic entrepreneurship and innovative engagement by Internet companies like Google is so significant. This new approach seeks to engage and empower the Cuban people directly while accepting some collateral benefit for the Cuban government, instead of aiming to undermine the government with a ham-handed embargo while accepting the collateral damage that such a policy inevitably has on the people.
Now that this approach has been reinforced by the Obama administration’s momentous decision to diplomatically engage Cuba as a way to further empower the Cuban people (making their lives, in the words of the president, a bit more fácil), the ball is clearly in Castro’s court.
Will he transform his initial economic reforms and marginal expansion of the Internet into change Cubans can believe (and even invest) in?