It is essential to deepen the reforms where reality has shown that what has been done is not enough. Delaying that deepening is not healthy, as we know.
Juan Triana Cordoví
ON CUBA Newws, December 29 2021
| Original Article: Cuban Economy in 2022 |
The good news that the decline in the national economy has stopped thanks to the good performance of the second and third quarters of this year, is doubly good because in general and due to the seasonal nature of our economy the first and the last quarter of each year are the busiest. So in 2021, that performance has changed.
It is also good news that a growth of 4% is planned for 2022, something that will require a significant effort if we take into account that the recovery conditions of the international economy are still far from reaching the years preceding COVID-19; that world inflation, and especially in the United States, seems to be turning into a big headache; and that world trade will continue to suffer from excessively expensive freight, a shortage of containers and high prices for them; foreign investment will continue to have a weak recovery and tourism flows on a world level will still be far from what they were three years ago.
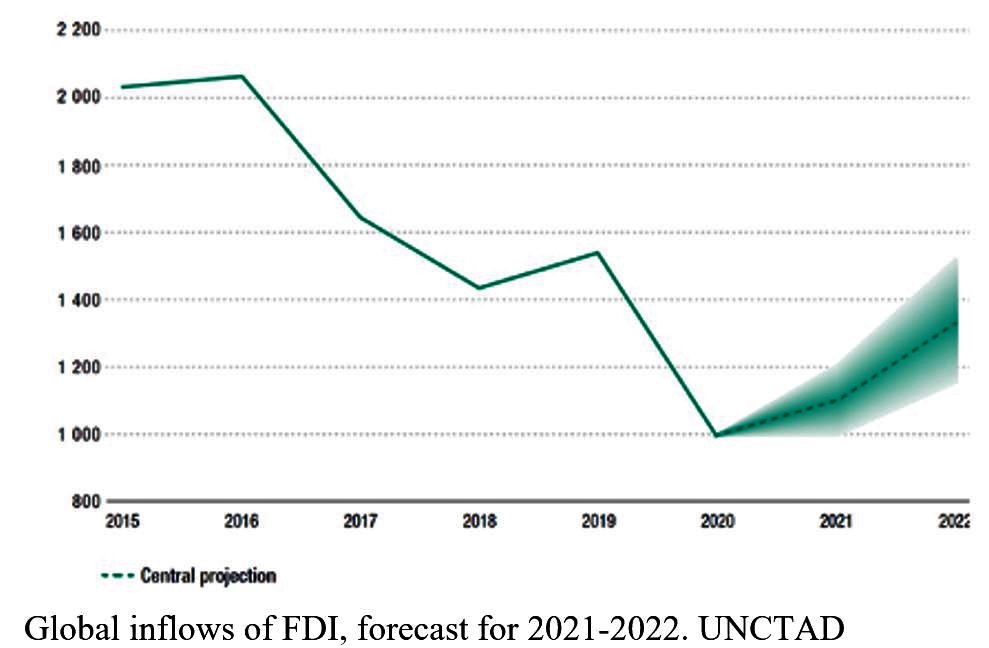
Global inflows of FDI, forecast for 2021-2022. UNCTAD
Macroeconomic stability
Growth is much more than a goal, a slogan or an exhortation, and having done a good planning exercise is not enough. It is necessary to achieve a minimum of macroeconomic stability that reduces uncertainty for all economic agents, that guarantees that the rules of the game will be followed, that discretion will have adequate limits, that the adjustment will produce the necessary changes at the microeconomic level to transform the business system, clean it of inefficient enterprises — because not all those that are in losses are — and that the allocation of resources is guided by efficiency criteria. Efficiency and productivity must be rewarded, and the costs of this adjustment must be cushioned with adequate policies. Condemning efficient enterprises to losses is not the best decision in a country that needs to purge its production system.
Inflation, what to do?
Much has been written about inflation in Cuba this year. Today it is the factor that generates more instability, uncertainty, a reduction in the purchasing power of “reorganized” wages and, logically, social unrest. At least we economists know that speculation is not its cause, in the same way that we know that appealing to the good faith of sellers will not solve, even momentarily, this scourge.
Three exchange rates instead of one, as the design promised, the reincarnation of the CUC in the freely convertible currencies whose access is more restrictive and a passive monetary policy are among its monetary causes. If reality surpassed the design, then the design must be adapted to this new reality.
The other cause is historical, secular and structural, the insufficient supply that has accompanied us since the early 1960s, due to the weak production system and restrictions to import, especially as of the 1990s. Generating a significant increase in supply keeping in mind a speedy recovery of the production system does not seem achievable (500 state companies in losses, and 67% of cooperatives in an “unfavorable” situation indicate the opposite). Production, even in those economies that function with high dynamism, lags behind in relation to demand, it is less elastic in the face of a variation in income. It will not be there where in the short term prices can be dealt with. Improperly regulating them produces worse effects, it has also been proven. The other component of the supply remains, imports, also limited in the state sector by the availability of foreign exchange. But there are reservations and they involve sharing the consumer market and encouraging non-state agents — national and non-national — to have a greater participation and share the risks.
Consolidating and deepening the reforms
In the annual seminar of the Center for the Study of the Cuban Economy, my colleague Antonio Romero synthesized the characteristics of the environment we will have for 2022, taking into account the performance of recent years:
- Deep drop in global economic activity in 2020. Record for some regions/countries.
- Strong recovery process since late 2020/early 2021 in most regions/countries.
- The per capita income levels reached in December 2019 will not be exceeded until 2023.
- Asymmetric recovery, and with great risks/uncertainties:
- a) Recurrence of outbreaks/peaks of the pandemic
- b) High and rising inflation for some sectors/markets
- c) Dangers of the process of reducing monetary stimuli (liquidity) by the main central banks
- Tensions in the international energy market
- Problems with some supply chains/logistics internationally
- Growing conflict between major global actors (USA, China, EU and Russia).
Inflation in the United States and Mr. Biden’s “forgetting” his pre-election promises are the other two factors that complicate the national situation.
And at the same time he pointed out the opportunities that this same evolution offered to our country:
- -Increase in demand for goods and services in foreign partners,
- -Increase in the price of some basic export products (sugar and nickel) and
- -Revaluation of the health industry (especially the strategic importance of vaccines).
Sugar prices have gone up by 38% from January to October 2021. It is true that our restriction is on production. Save the sugarcane industry! The phrase deserves more than one book. Saving the sugar industry is not recovering it, it is making it new, from the furrow to the shipping terminal. From 2016 to 2020, this industry received investments of 1.035 billion dollars, less than the trade sector (1.563 billion and not to mention 15.541 billion in the real estate sector). Year after year we witness a new unfulfilled plan to recover the sugar industry, hopefully, this time it will be different.
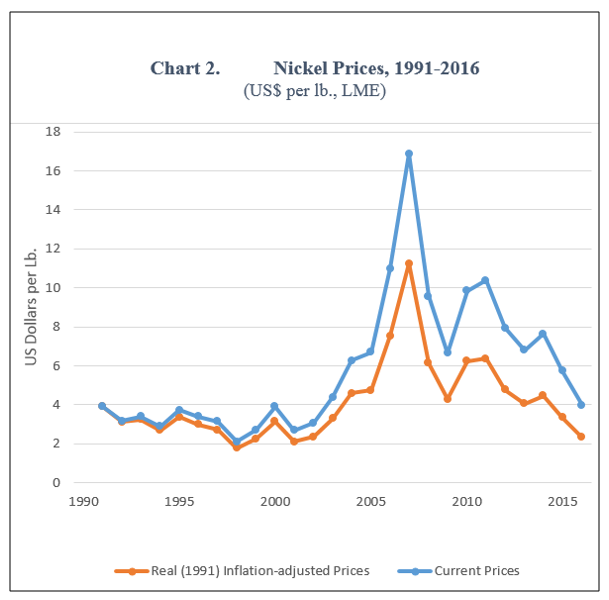
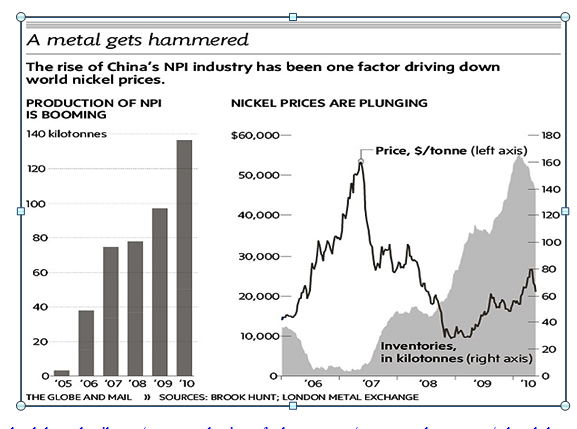
Nickel prices also offer an opportunity (37% increase in their prices from January to October) and world demand seems to maintain a certain dynamism. Our limit is once again in the productive capacity. Mining was allocated 1.413 billion in the same period and not everything was for nickel mining.
Undoubtedly the greatest opportunity could be in the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries. Despite the complicit silence of some international institutions regarding Cuban vaccines, it is indisputable that today it is our greatest strength in the industrial sector.
The recovery of tourist flows on a global scale will depend on the performance of the pandemic, which has once again shown its face in the omicron variant and complicates our source markets again.
World foreign investment flows will not reach the dynamics of before 2019. Competing for scarce flows with other markets is a difficult task. It is true that something has been announced in relation to FDI, but it seems that time does not count and the necessary reform of requirements and procedures did not arrive in 2021. It is not enough to recognize that “the little progress is not attributable only to the difficulties generated by the blockade and, in the last two years, by the international crisis derived from the COVID-19 pandemic, but also internal factors.” And if we know which ones, then why don’t we just eliminate them?
Because there are external factors on which there is no way to influence to achieve favorable changes to our economy, because there are structural failures that will not be resolved in the short term; consolidating the reforms will be decisive. It is a difficult exercise that requires many means, from the timely and adequate coordination of actions and organizations to the competence of the people who work in it; also agreeing to pay unavoidable costs until the resizing of the state business sector is promoted, not only in terms of its size, but also in the way it operates in the economy. This exhortation to achieve greater autonomy must be made really effective. And also that other that demands a greater relationship with the private and cooperative business sector. More than a thousand SMEs in three months, in the worst conditions in which an enterprise can be born, is enough to understand how dynamic this sector can be. More effective support, better incentives — especially tax incentives —, less prejudice and greater spaces for action are still necessary.
Today there are more than seven hundred local development projects. Local governments should understand that having more local development projects and promoting a greater number of small and medium-sized enterprises is decisive for the prosperity of their municipalities. Thinking of the local as the small, as the complementary, does not seem to be the best option. “The local is not the utopia of a development from the small, but the construction of capacities from the territory to promote sustainable development at the municipal, regional, national and international level”1 It is necessary to take a look at the curb of the well and look from there inward and outward.
It is essential to deepen the reforms where reality has shown that what has been done is not enough. Delaying that deepening is not healthy, as we know.
If a 4% growth is achieved, we will still be very far from the growth dynamics we need, far even from what was achieved in a year like 2019 and we all know that even in that year our production was not able to adequately satisfy that part of the demand that depended on it. It will be good to grow and it will be better if all Cubans manage to perceive it.
Note:
1 Carrizo Luis and Gallicchio Enrique (2006): “Desarrollo local y gobernanza. Enfoques transdisciplinarios. Investigación y políticas para el desarrollo en América Latina,” Uruguay, Latin American Center for Human Economy, CLAEH.
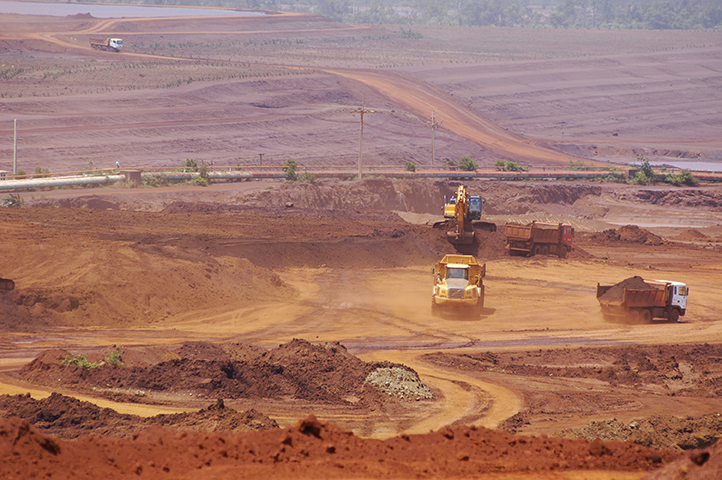




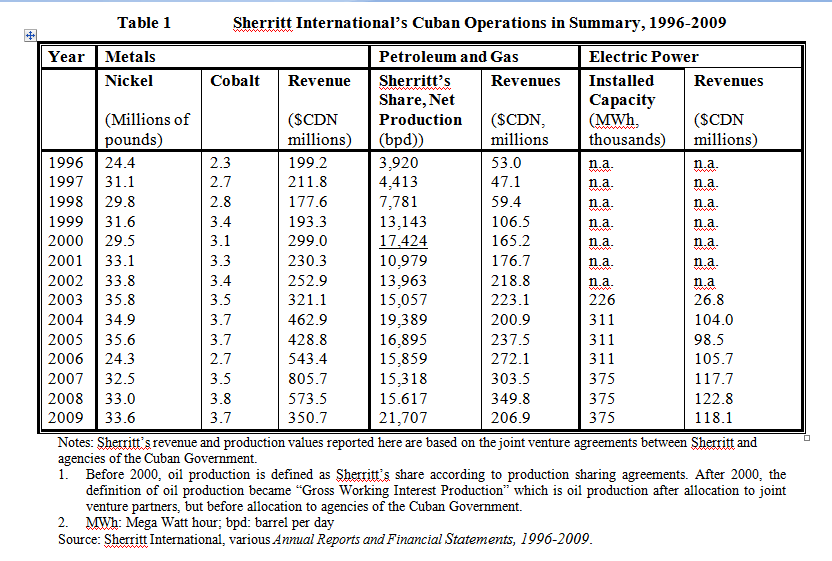
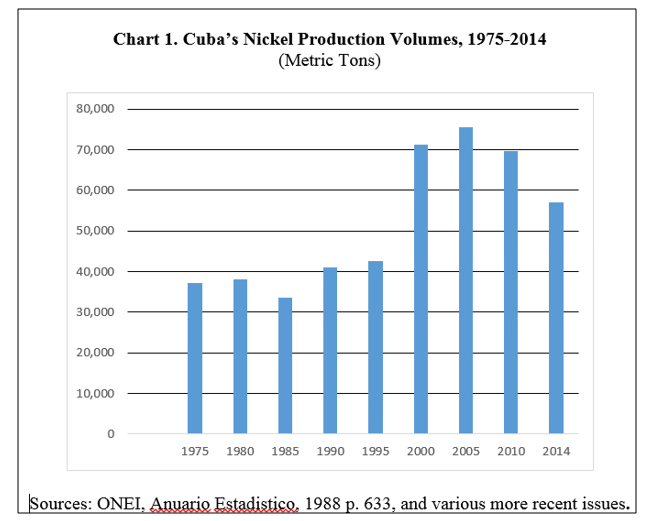 The Government of Cuba is now the joint owner of a vertically integrated nickel operation, from extraction and concentrating through to refining and international marketing. Cuba also has obtained new technologies and managerial skills for oil and gas extraction and utilization, as well as electricity generation. Cuba’s nickel reserves are fifth largest in the world and production volumes are 10th largest.
The Government of Cuba is now the joint owner of a vertically integrated nickel operation, from extraction and concentrating through to refining and international marketing. Cuba also has obtained new technologies and managerial skills for oil and gas extraction and utilization, as well as electricity generation. Cuba’s nickel reserves are fifth largest in the world and production volumes are 10th largest.