By Arch Ritter
As Cuba moves towards a mix of economic institutions with a greater role for the market mechanism as a means of social control over economic activity as well as for private ownership, various forms of co-operative organization have some appeal. Among the many forms of cooperative enterprise that exist and could be considered by Cuba, the Home Hardware variety may have a useful role to play. Already some academic analysts in Cuba are exploring the varieties of cooperative and their relevance for Cuba. ( See New Publication from Cuba: Cooperativas y Socialismo: Una Mirada DesdeCuba).
The Home Hardware Cooperative Model
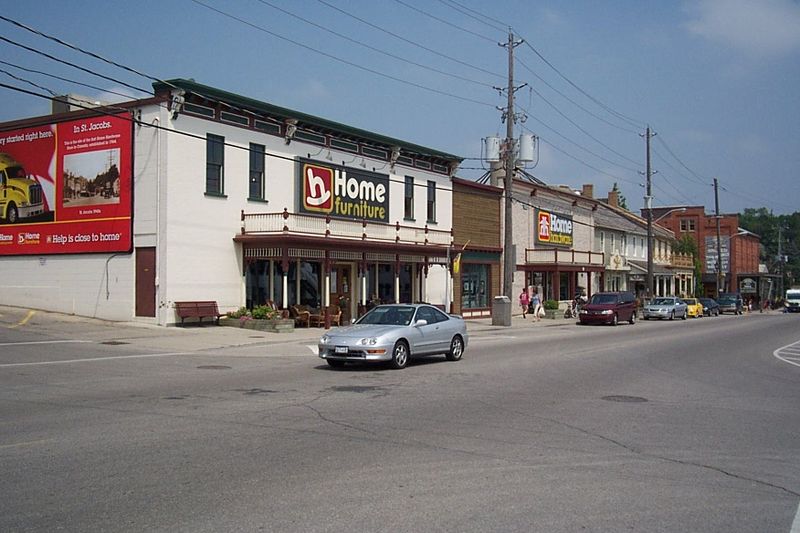
Home Hardware, is a dealer-owned cooperative, in which about 1000 individual hardware store-owners also own the larger enterprise. Membership in the cooperative permits the store owners to obtain major economies of scale in terms of purchasing and shared buying power, advertising, comprehensive inventory management and product delivery, and store management techniques. The cooperative has permitted small owner-operated hardware stores to remain viable in small towns and urban neighborhoods. It has permitted them to survive and thrive in the face of the competition from the massive “Big Box” hardware stores such as Rona (in Canada), Home Depot, Lowe’s Companies Inc., or even Wal-Mart.
Original Home Hardware Store, now “Home Furniture”, St. Jacobs Ontario
The establishment of the Home Hardware co-operative was spear-headed by Walter Hachborn starting at the Hollinger Hardware store in the small town of St. Jacobs Ontario in 1938, working as a stock boy for $8 per week. When Gordon Hollinger died in 1948, Walter took over many of his responsibilities, and purchased the store in partnership with Henry Sittler and Arthur Zilliax in 1950. Hachborn then undertook the difficult task of persuading his fellow retailers to join forces in the Home Hardware’s cooperative – a task requiring diplomacy and determination. (Hachborn, who – full disclosure – is my Father’s cousin, was awarded “The Order of Canada” as well as the “Queen’s Golden Jubilee Medal” in tribute to his business achievements and community service.)
Relevance for Cuba – and Any Country
The Big Box chains exist because of their economic advantages, namely economies of scale in purchasing, marketing and advertising, and management systems plus bargaining power in their relationship with their workers. However there are also a variety of major disadvantages of the Wal-Mart type of Big Box model of retailing or of the “Starbucks” model of service provision. Among these are:
1. Major concentrations of income and wealth in the hands of the few owners of the chains. (The Walton family members have estimated assets of $US 92 billion making then the wealthiest family in the world. )
2. Damage to local communities and neighborhoods as commercial live gets sucked out of them to the sites of the Big Box stores.
3. Environmental costs as long distance driving to the big stores replaces closer access to community stores.
4. Exclusion of smaller scale local sources of products in favor of massive low-cost purchases for all their stores from single sources – usually from China, thereby helping to kill off local producers.
5. Unpleasant shopping experience, (e.g. wandering around large spaces looking for a particular item with no assistance or guidance to be found.)
Already Cuba has a number of state-owned chains of stores,restaurants and hotels such as Tiendas Universo (CUBANACAN S.A.), Tiendas Panamericanas (CIMEX S.A.), Tiendas Caracol (HORIZONTES Hoteles S.A.), Tiendas y Supermercados de la Sociedad Meridiano S.A. (CUBALSE Corporation; closed in 2009), Tiendas TRD Caribe (GAVIOTA S.A. owned by the militayr), and Tiendas de Habaguanex. If these were to be privatized under concentrated ownership, some of the problems of the Wal-Mart or Starbucks types of conglomerate would be generated or continued.
In the years ahead, it is likely that Cuba will continue to move towards greater private ownership in many areas. If a future government wishes to avoid some of the disadvantages of the Mammoth Enterprise Chain syndrome, it could consider providing encouragement to Cuban-owned cooperative networks or independent enterprises in various activities in retailing and service provision. Possible areas where such a form of organization could be useful might include hardware stores (of course), food stores, bars, coffee shops, variety stores, barber shops, estheticians services and clothing stores, among others.


![TIENDADELCIMEX[1]](https://thecubaneconomy.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/10/TIENDADELCIMEX1.jpg)