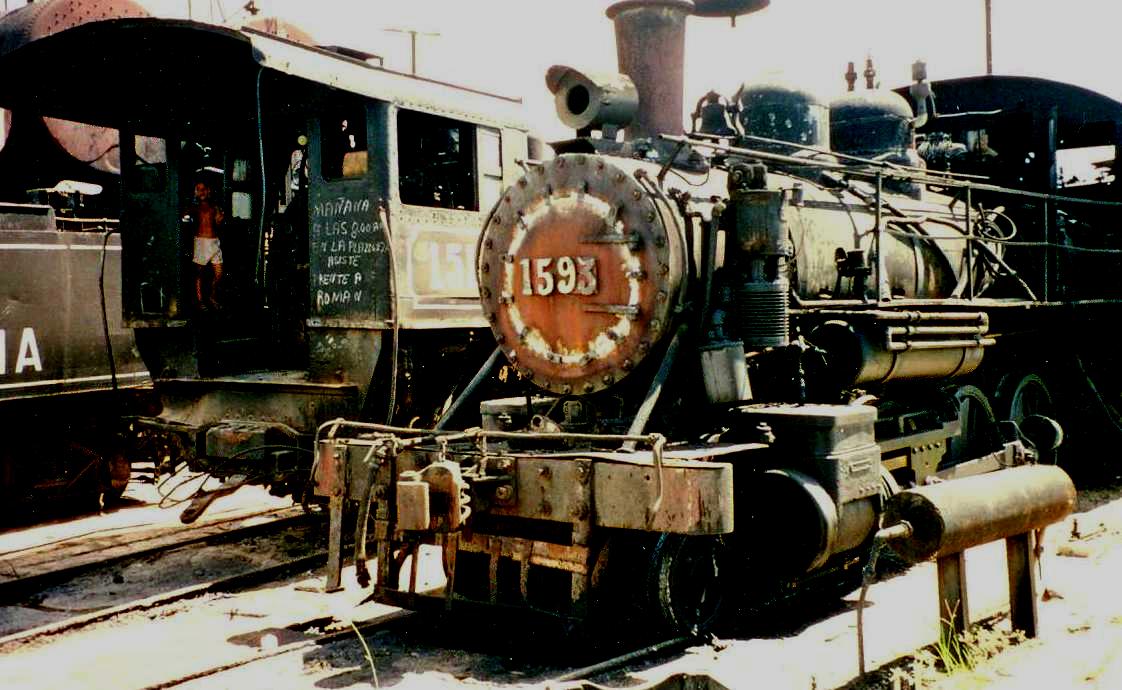(Reuters).—The Brazilian giant Odebrecht plans to produce sugar in Cuba, the company reported Monday in the first injection of foreign capital in a sector so far closed in the communist-ruled island.
Steam Locomotives at the now defunct Australia sugar mill, November 1994, photo by Arch Ritter
Odebrecht Group signed with the state of Cuban Sugar Business Administration a “productive management contract” to wit “September 5” in the central province of Cienfuegos.
“The agreement for a period of 10 years is to increase sugar production and milling capacity and help the revitalization” of the industry, Odebrecht said in an email sent to Reuters through his press office.
The project would open to foreign capital, the underfunded Cuba’s sugar industry, whose production has plummeted from about 8.0 million tons in the 1970s to just 1.2 million tonnes in the last harvest. In addition, it will deepen Brazil’s role in modernizing the dilapidated productive infrastructure of the island.
Odebrecht did not elaborate.
But a Brazilian sugar industry executive told Reuters that the contract could be signed this week during a visit to Cuba, Brazilian President Dilma Rousseff. Cuba allowed more than a decade, the inflow of foreign capital to develop other strategic industries such as tourism and oil recently, where a consortium led by Repsol-YPF this year will begin to explore Cuban waters in the Gulf of Mexico.
Private companies from other countries have spent years negotiating its entry into the sugar industry in Cuba, nationalized shortly after Fidel Castro’s revolution in 1959. The opening comes after a major restructuring of the industry in late 2011 as part of the efforts of President Raul Castro to modernize the island’s socialist economy.
Do you also ethanol?
According to the director of the Brazilian sugar industry with knowledge of the project, Odebrecht also produce ethanol from biomass energy in Cuba. “Cuba is opening up the possibility of producing ethanol accompanied by power generation and Odebrecht will mount a distillery there,” said the businessman.
“It’s a similar project that Odebrechtis developing in Angola,” he added in reference to a joint venture of $ 258 million Angolan oil company Sonangol with to produce some 260,000 tons of sugar, 30 million liters of ethanol and 45 megawatts of power power.
Ethanol production on a large scale in Cuba has met with opposition from former President Fidel Castro, an ardent critic of the use of food crops like corn to make biofuels. Some experts believe that if Cuba could revive its sugar industry to become the third largest producer of biofuels in the world behind the United States and Brazil.
Ron Soligo, an economist at Rice University in Houston who has studied Cuba’s sugar industry, estimates that the island could produce about 7,500 million liters of ethanol annually. “But developing the ethanol industry in Cuba will take a while, since much of the land has been abandoned for years,” he said.
“Due to the centralized nature of the Cuban economy, a large Brazilian company can be the right partner,” he added.
Brazil, the second largest ethanol producer in the world, has provided technical assistance the Cuban authorities for the production of biofuels from sugar cane. “The issue is on the table. There is planned investment in sugar and there is a possibility that at some point this can be extended to the ethanol industry,” said a Brazilian Foreign Ministry source.
Odebrecht’s entry in the modernization of the depressed sugar industry expand its role in the infrastructure of the island. The company is currently one of the leading ethanol producers in Brazil through its subsidiary ETH.
Brazilian construction works executed for 800 million dollars to upgrade the container port of Mariel west of Havana. The project largely funded by the government’s National Development Bank of Brazil is seen as a key business platform if the U.S. lifts its embargo on the island.
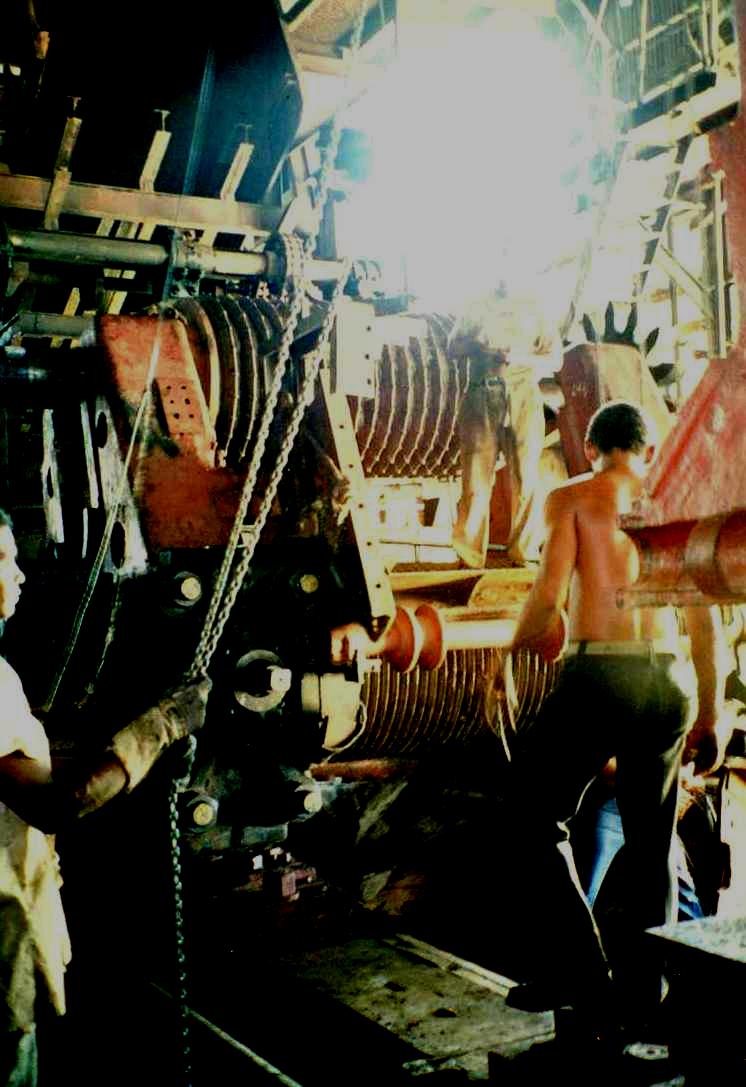 Repairs, at the now defunct Australia sugar mill, november 1994, Photo by Arch Ritter
Repairs, at the now defunct Australia sugar mill, november 1994, Photo by Arch Ritter