Cuba: When bureaucrats attack
The abrupt closing of a popular Havana business tests Raul Castro reforms.
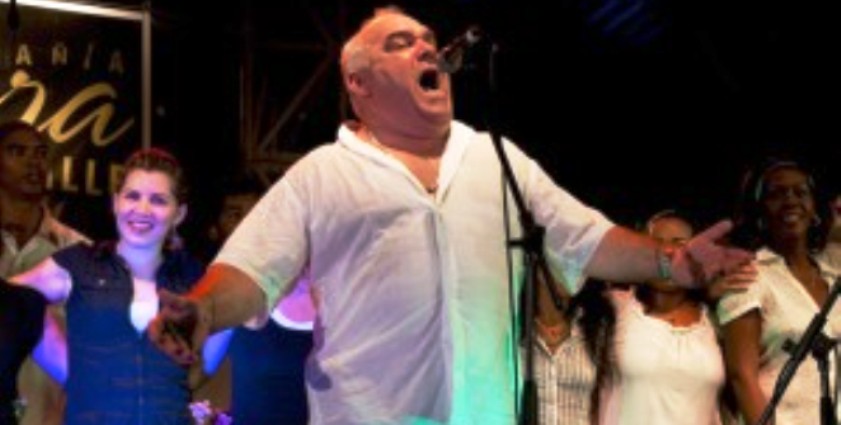

Ulises Aquino
Original here: Cuba: When Bureaucrats Attack
Nick Miroff, July 31, 2012 08:44
HAVANA, Cuba— In the new Cuba, the one President Raul Castro and his team of reformers say they’re building, the hard-working entrepreneur is a patriotic figure, a job-creator who’s helping to lift up the island’s feeble economy.
That’s the Cuba where Ulises Aquino thought it would be a good idea to start a business.
With funds earned abroad as an award-winning opera singer, Aquino opened a restaurant and cabaret last year where the company he founded, Opera de la Calle (Opera of the Street) could perform.
He called it “El Cabildo” (roughly, the “meeting place”), transforming a trash-strewn lot into a lively entertainment venue, with an open-air stage, restaurant and bar. Aquino offered free children’s theater and other community activities on weekend mornings, and kept his prices low, charging $2 admission to Opera of the Street shows that feature as many as 80 singing-and-dancing performers.
Aquino was a good socialist businessman too, sharing profits with his 130 employees and paying wages that were three or four times the $20 average monthly Cuban government salary.
More from GlobalPost: Cuba mute in the time of cholera
El Cabildo was so innovative that Aquino and his new model of socialist enterprise were featured in a July 12 Reuters article titled “In Cuba, an opera singer builds an empire.”
And that’s when the bureaucrats attacked.
“It may have been the last straw,” said Aquino, of the article. “But they had their eye on me for a while.”
The following Saturday night, on July 21, a team of city government inspectors arrived at El Cabildo and interrupted the show, “like a team of commandos,” said Aquino, a barrel-chested bulldog of a man, who trembled with anger as he re-told the story.
The inspectors ordered Aquino off the stage as the audience looked on in shock. Then they shut down the kitchen and froze the cash register for a four-hour inspection.
By the following Monday El Cabildo was closed and Aquino had an order from local Havana officials stripping him of his business license for two years.
The inspectors had determined El Cabildo to be in possession of “more chairs than the permitted number,” and “products whose origin could not be determined” – ie lacking receipts. Two prep cooks who Aquino says were there on a trial basis were found to be “illegal workers.”
Worst of all, Aquino was accused of “enrichment” because he was charging a $2 cover “for personal benefit,” something he was not specifically authorized to do—even though entertainment venues all over Havana routinely charge $5 to $10 at the door.
There was no fine, no appeals process, no legal recourse. It didn’t seem to matter that Aquino had more than $100,000 of his savings invested in the business, or that 130 families would lose their income.
This was the old way in Cuba, where bureaucrats rule.
More from GlobalPost: Cuba’s gay rights revolution
Aquino, for one, doesn’t blame Raul Castro. “This goes completely against everything that the government has been telling us,” he said.
“The people who are behind this are the mid-level bureaucrats who know the status quo is endangered by all these new opportunities that offer a change from all the old taboos and prohibitions,” said Aquino.
On Monday, officials from Cuba’s Ministry of Culture issued a statement offering their support for Aquino’s Opera company and its ability to continuing performing at El Cabildo. But they said nothing about his dispute with city authorities and the fate of the businesses that make Opera of the Street possible.
“This place is dead right now,” said Ruben Rodriguez, the opera company’s choreographer, covering up the sound board and lighting controls opposite an empty stage. “Everything’s paralyzed.”
The fate of El Cabildo will be closely watched in Cuba, where Raul Castro’s economic reform process has lost momentum in recent months and Cubans’ initial enthusiasm for starting small businesses has faded.
Officials announced a new pilot program last week that will convert state-run companies into employee-run cooperatives, but the experiment will be limited to just 222 firms.
Meanwhile, a vast state apparatus of government officials who produce nothing of value remain ready to prey upon those who do.
Castro and other Cuban officials have repeatedly said that recalcitrant bureaucrats will not be allowed to stand in the way of economic change. If they intervene to help re-open El Cabildo, they will send a clear signal that Cuba’s new small businesses deserve encouragement, not strangulation.
But if El Cabildo stays closed, it can send a different message about Cuba’s incipient capitalism in Cuba: that new entrepreneurs here should not be too ambitious with their plans or too proud of their success. And any business, no matter how big, can be shut down on a whim, if a local official orders it so.
In that case, Aquino said, “the loser here won’t be me. It’ll be our country.”
 Opera de la Calle
Opera de la Calle
See also Havana Times July 27, 2012, Cuba Closes ‘Street Opera’ Project