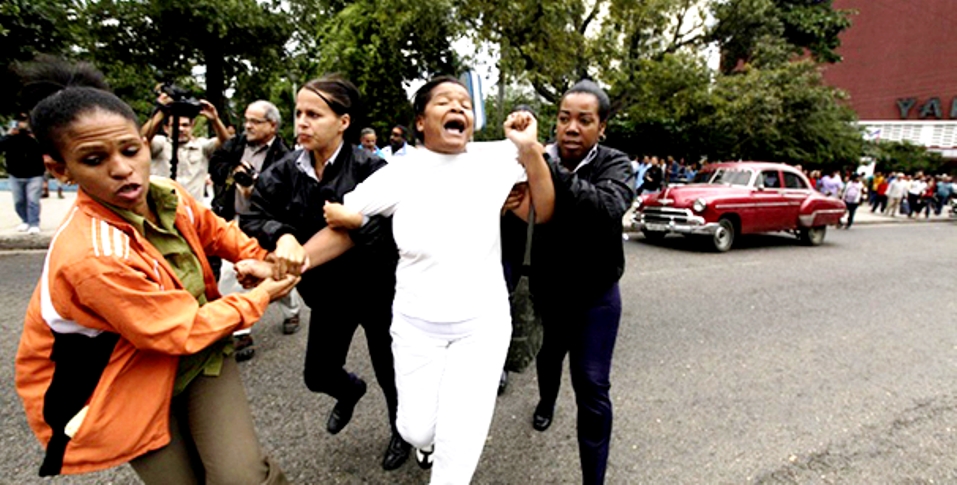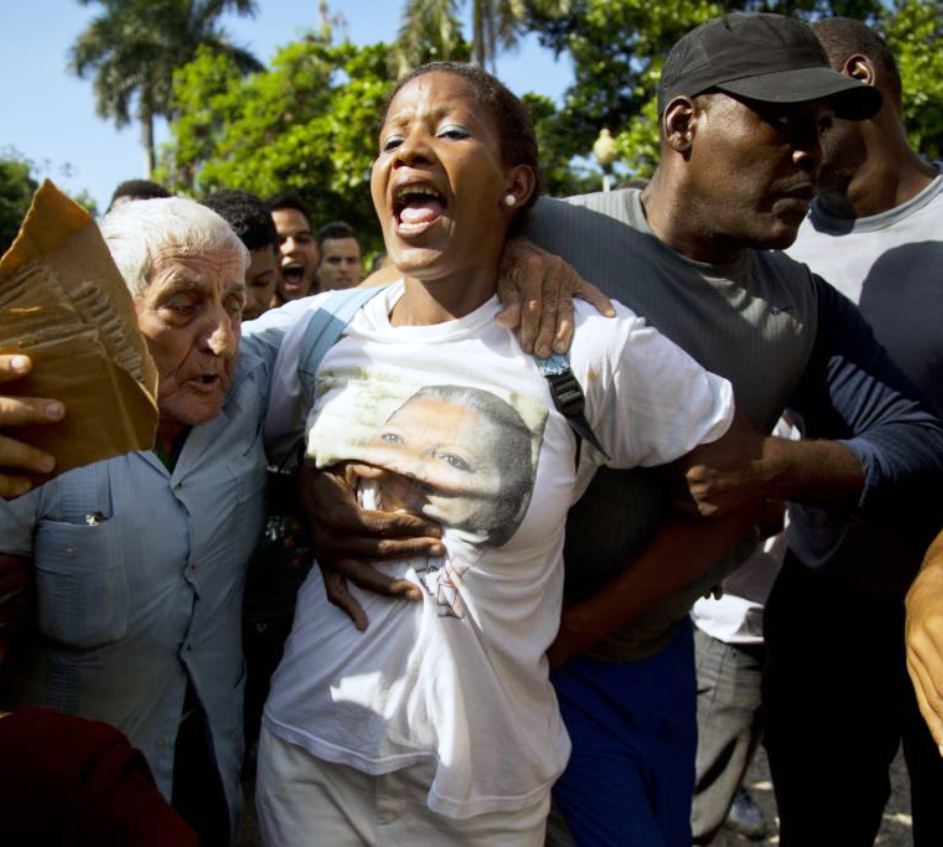Original here: HUMAN RIGHTS WATCH 2015: CUBA
The Cuban government continues to repress dissent and discourage public criticism. While in recent years it has relied less on long-term prison sentences to punish its critics, short-term arbitrary arrests of human rights defenders, independent journalists, and other critics have increased dramatically. Other repressive tactics employed by the government include beatings, public acts of shaming, and the termination of employment.
In December 2014, President Barack Obama announced that the United States would normalize diplomatic relations with Cuba and ease restrictions on travel and commerce with the island in exchange for several concessions by the Cuban government, including a commitment to release 53 political prisoners and to allow visits by international human rights monitors.
Arbitrary Detentions and Short-Term Imprisonment
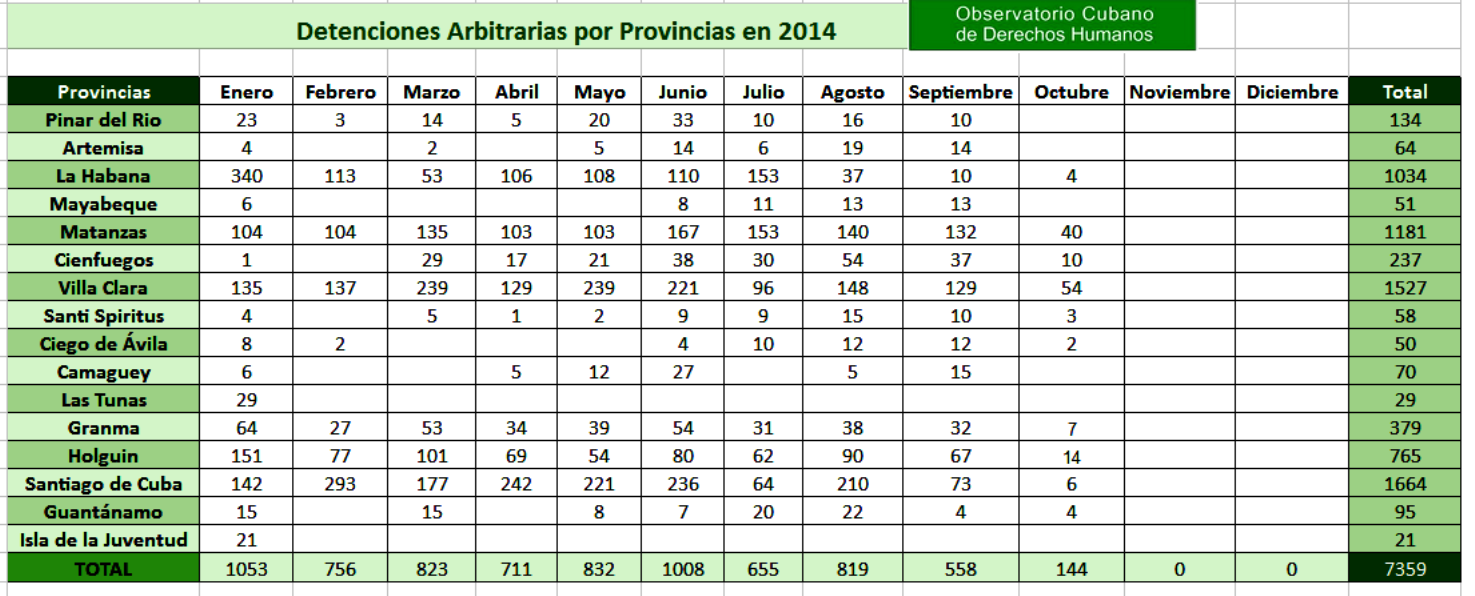
The government continues to rely on arbitrary detention to harass and intimidate individuals who exercise their fundamental rights. The Cuban Commission for Human Rights and National Reconciliation (CCDHRN)—an independent human rights group the government views as illegal—received over 7,188 reports of arbitrary detentions from January through August 2014, a sharp increase from approximately 2,900 in 2013 and 1,100 in 2010 during the same time period.
Security officers virtually never present arrest orders to justify the detention of critics and threaten them with criminal sentences if they continue to participate in “counterrevolutionary” activities. In some cases, detainees are released after receiving official warnings, which prosecutors can then use in subsequent criminal trials to show a pattern of delinquent behavior. Dissidents said these warnings aim to discourage them from participating in activities seen as critical of the government.
Detention is often used preemptively to prevent individuals from participating in peaceful marches or meetings to discuss politics. In the days leading up to the summit meeting of the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC), for example, which took place in Havana on January 28 and 29, 2014, at least 40 people were arbitrarily detained, and 5 held under house arrest until the conference had ended, according to the CCDHRN.
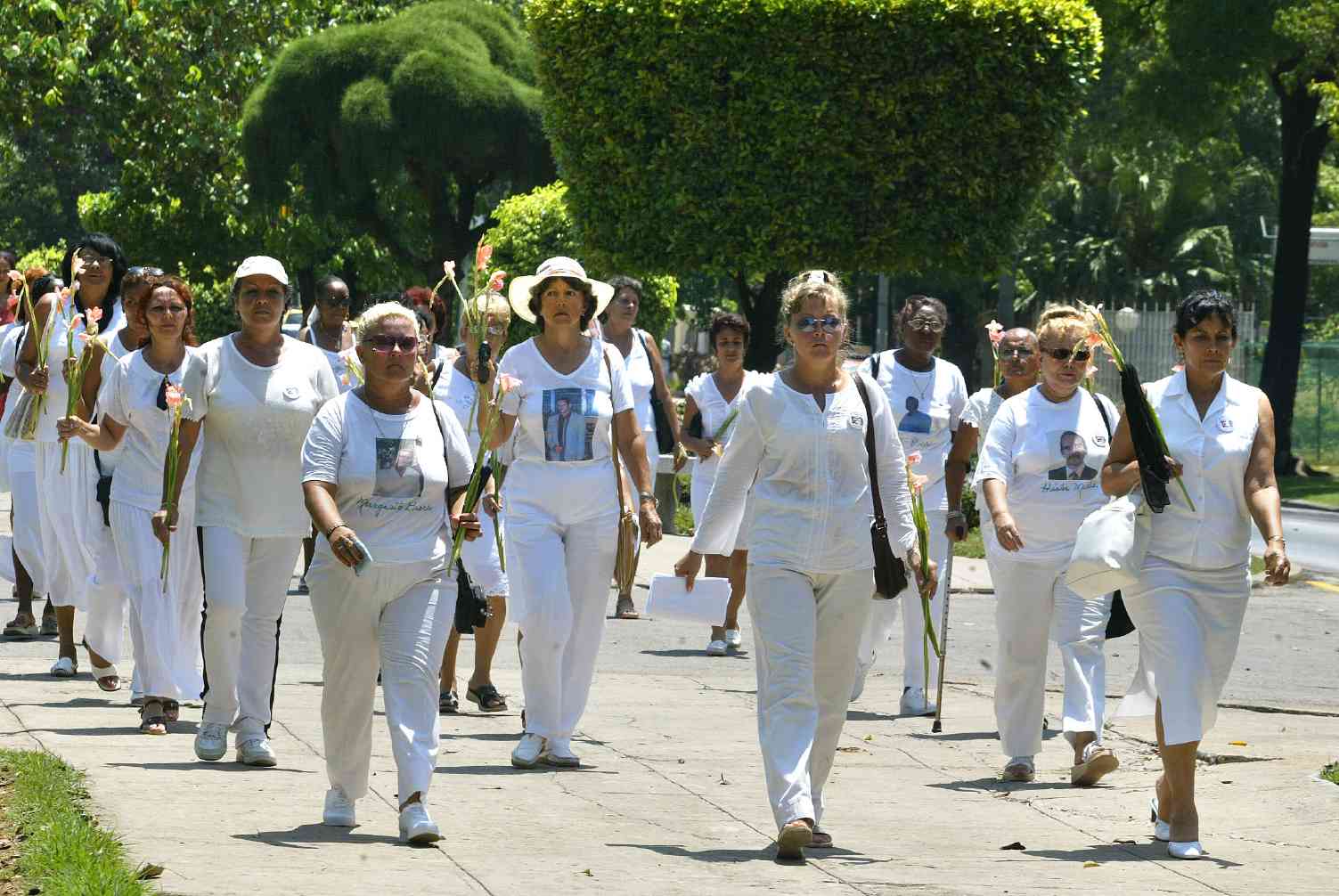
Members of the Damas de Blanco (Ladies in White)—a group founded by the wives, mothers, and daughters of political prisoners and which the government considers illegal—are routinely detained before or after they attend Sunday mass. On May 4, for example, more than 80 women were detained before attending mass throughout the island. On July 13, 129 members of the group were detained as they prepared to attend commemorative ceremonies honoring Cubans who died attempting to leave the island in 1994.
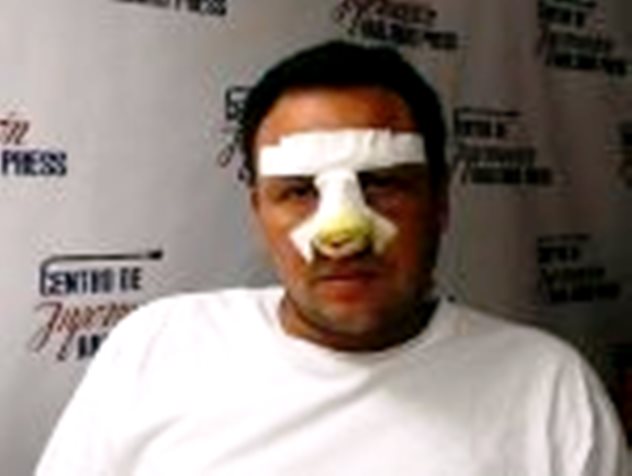
Detainees are often beaten, threatened, and held incommunicado for hours and even days. The former political prisoner Guillermo Fariñas, who was placed under house arrest for the duration of the CELAC conference and then arrested when he attempted to leave home, reported suffering two broken ribs and other injuries as a result of a beating he received while in detention. Yilenni Aguilera Santos, a member of the Damas de Blanco movement in Holguín, reported suffering a miscarriage when security agents subjected her to a severe beating after arresting her on her way to mass on June 22.
Political Prisoners
Even after the conditional release of dozens of political prisoners in December 2014, dozens more remain in Cuban prisons according to local human rights groups. These groups estimate that there are more political prisoners whose cases they cannot document because the government prevents independent national or international human rights groups from accessing its prisons.
Cubans who criticize the government continue to face the threat of criminal prosecution. They do not benefit from due process guarantees, such as the right to fair and public hearings by a competent and impartial tribunal. In practice, courts are “subordinated” to the executive and legislative branches, denying meaningful judicial independence.
Freedom of Expression
The government controls all media outlets in Cuba and tightly restricts access to outside information, severely limiting the right to freedom of expression. Only a very small fraction of Cubans are able to read independent websites and blogs because of the high cost of, and limited access to, the Internet. While people in cities like Havana, Santiago de Cuba, or Santa Clara have access to the Internet, people in more rural areas are not able to go online.
A May 2013 government decree directed at expanding Internet access stipulates that the Internet cannot be used for activities that undermine “public security, the integrity, the economy, independence, and national security” of Cuba—broadly worded conditions that could be used against government critics.
A small number of independent journalists and bloggers manage to write articles for websites or blogs, or publish tweets. Yet those who publish information considered critical of the government are sometimes subject to smear campaigns, attacks, and arbitrary arrests, as are artists and academics who demand greater freedoms.
In May 2014, blogger Yoani Sanchez launched the website 14ymedio, Cuba’s first independent online newspaper. Within hours, the site was hacked, and visitors were directed to a page dedicated to scathing criticisms of Sanchez. The site was restored the following day, but blocked again several days later, and has remained inaccessible to Internet users within Cuba ever since.
In May 2013, the director of the government-run Casa de las Americas cultural institute, Roberto Zurbano, published an article in the New York Times highlighting persistent inequality and prejudice affecting Afro-Cubans. He was subsequently attacked in the government-controlled press and demoted to a lesser job at the institute.
Travel Restrictions and Family Separation
Reforms to travel regulations that went into effect in January 2013 eliminate the need for an exit visa to leave the island, which had previously been used to deny the right to travel to people critical of the government and their families. Since then, many people who had been previously denied permission to travel have been able to do so, including human rights defenders and independent bloggers.
Nonetheless, the reform included very broad discretionary powers that allow the government to restrict the right to travel on the grounds of “defense and national security” or “other reasons of public interest,” allowing the authorities to deny exit to people who express dissent. For example, authorities have repeatedly denied Manuel Cuesta Morúa the right to travel abroad since he attempted to organize a parallel summit to the CELAC conference in January 2014.
The government also continues to arbitrarily deny Cubans living abroad the right to visit the island. In August 2013, the Cuban government denied Blanca Reyes, a Damas de Blanco member living in exile in Spain, permission to travel to Cuba to visit her ailing 93-year-old father, who died in October before she could visit him.
The government restricts the movement of citizens within Cuba through a 1997 law known as Decree 217. Designed to limit migration to Havana, the decree requires that Cubans obtain government permission before moving to the country’s capital. It is often used to prevent dissidents from traveling there to attend meetings and to harass dissidents from other parts of Cuba who live in the capital.
Prison Conditions
Prisons are overcrowded, and unhygienic and unhealthy conditions lead to extensive malnutrition and illness. Prisoners are forced to work 12-hour days and punished if they do not meet production quotas, according to former political prisoners. Inmates have no effective complaint mechanism to seek redress, and those who criticize the government, or engage in hunger strikes and other forms of protest, are subjected to extended solitary confinement, beatings, restrictions on family visits, and denial of medical care.
While the government allowed select members of the foreign press to conduct controlled visits to a handful of prisons in April 2013, it continues to deny international human rights groups and independent Cuban organizations access to its prisons.
Human Rights Defenders
The Cuban government still refuses to recognize human rights monitoring as a legitimate activity and denies legal status to local human rights groups. Meanwhile, government authorities harass, assault, and imprison human rights defenders who attempt to document abuses.
Key International Actors
President Obama announced in December 2014 that the US government would normalize diplomatic relations with Cuba and ease restrictions on travel and commerce with the island. In exchange, the Cuban government committed itself to—among other things— releasing 53 political prisoners and allowing visits to the island by the International Committee of the Red Cross and UN human rights monitors.
President Obama also called on the US Congress to lift the economic embargo on Cuba. For more than half a century, the embargo has imposed indiscriminate hardship on the Cuban people and has done nothing to improve the country’s human rights record. The UN General Assembly has repeatedly called for an end to the US embargo on Cuba. In October 2014, 188 of the 192 member countries voted for a resolution condemning the embargo.
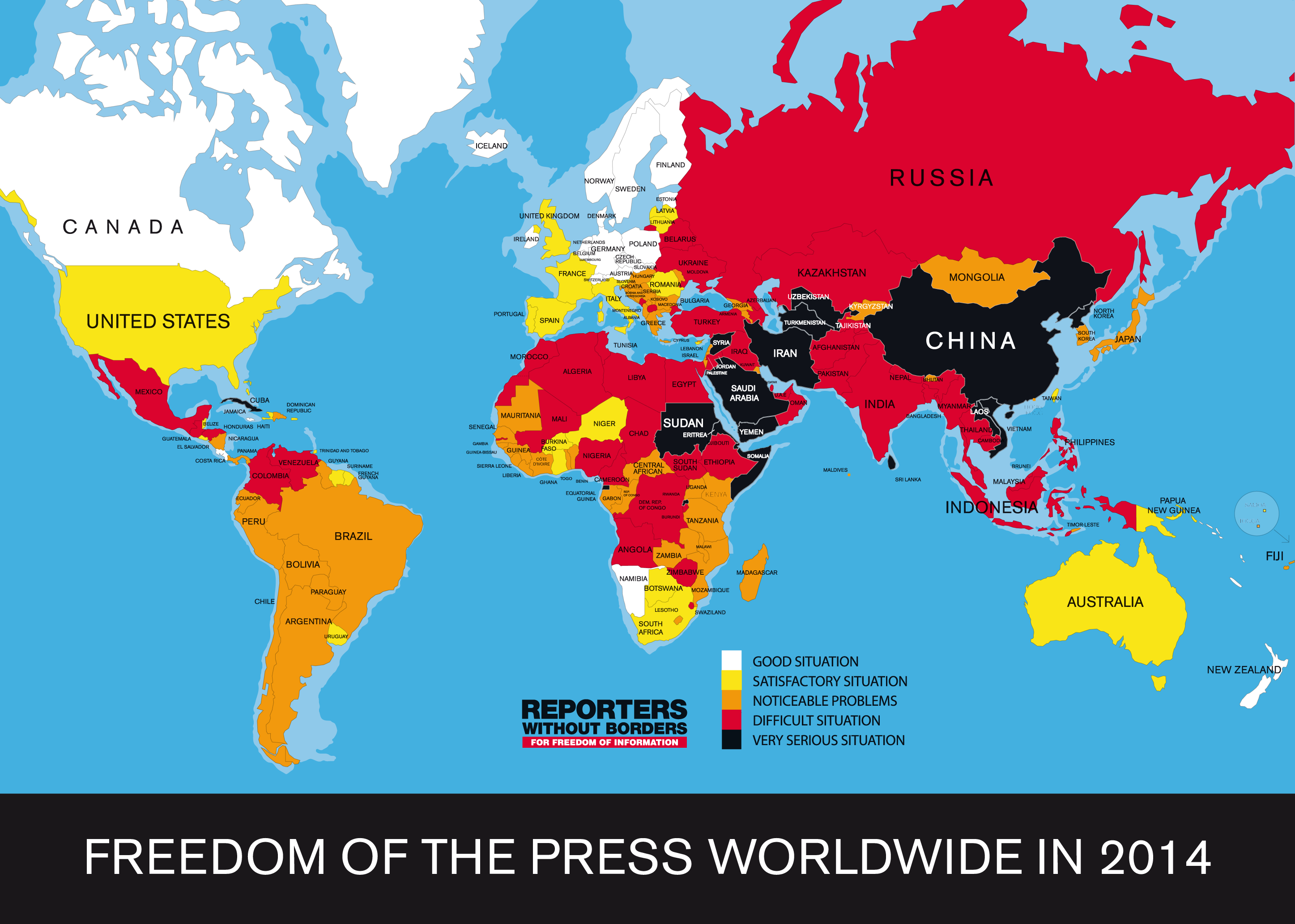
The European Union (EU) continues to retain its “Common Position” on Cuba, adopted in 1996, which conditions full EU economic cooperation with Cuba on the country’s transition to a pluralist democracy and respect for human rights. However, after a meeting in April 2014 in Havana, European Union and Cuban delegates agreed on establishing a road map for “normalizing” relations. EU officials indicated that concerns about civil liberties and democratic participation would continue to influence EU policy towards Cuba.
At the Organization of American States General Assembly in June, governments throughout the region called for the attendance of Cuba at the next Summit of the Americas in Panama in 2015.
In November 2013, Cuba was re-elected to a seat on the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC), defeating Uruguay for a regional position despite its poor human rights record and its consistent efforts to undermine important council work. As a UNHRC member, Cuba regularly voted to prevent scrutiny of serious human rights situations around the world, opposing resolutions spotlighting abuses in North Korea, Syria, Iran, Sri Lanka, Belarus, and Ukraine. Cuba, however, supported the landmark resolution on sexual orientation and gender identity adopted by the council in September 2014.
The text of the online 2015 World Report Cuba chapter has been updated from the print version to take into account events in late 2014.
Cuban security personnel detain a member of the Ladies in White group during a protest on International Human Rights Day, in Havana on December 10, 2014. © 2014 Reuters na on December 10, 2014. © 2014 Reuters