JOC, MAY 19, 2016
Greg Miller
Original Article: http://www.joc.com/port-news/international-ports/cuba-port-plans-be-transshipment-hub-after-us-lifts-embargo_20160518.html
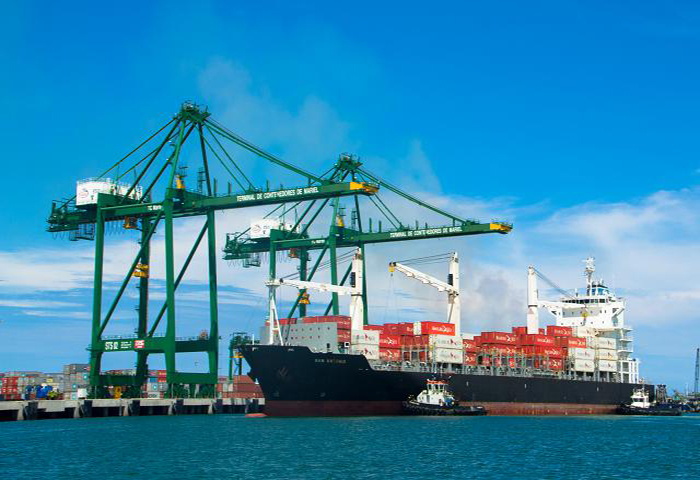
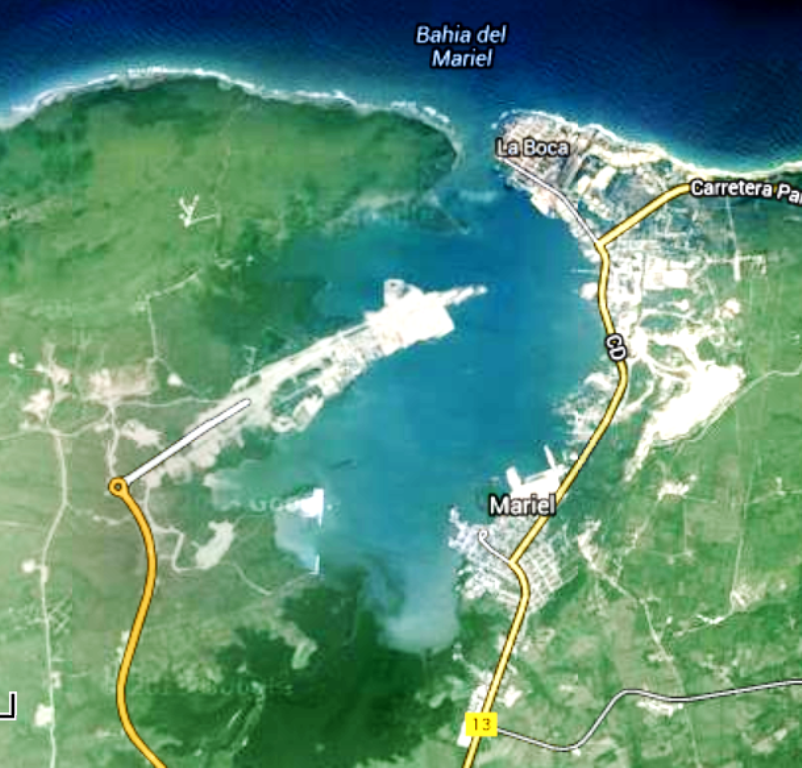
Cuba’s Mariel container terminal has already planned its transformation into a major transshipment hub after theU.S. trade embargo ends, according to TC Mariel General Director Charles Baker.
In an address to the Caribbean Shipping Association Executives’ Conference held near Port Canaveral, Florida, Baker described surging growth at TC Mariel, its short- and long-term expansion plans and strategy to diversify beyond domestic cargo into transshipment.
The PSA International-operated terminal opened in January of 2014. Throughput at Mariel grew 35 percent in 2015, reaching 330,000 twenty-foot-equivalent units, and is up 29 percent year-to-date this year as a result of Cuba’s “booming” tourism trade, Baker said.
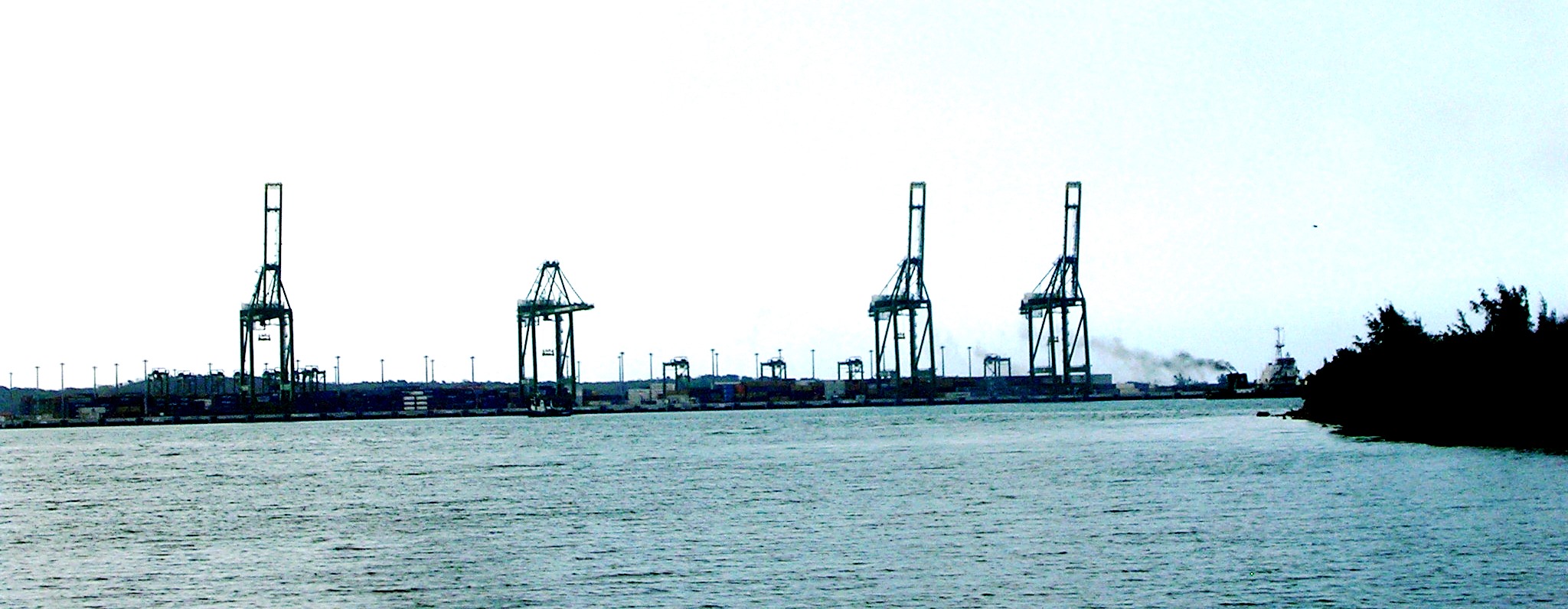
The container terminal has four gantry cranes, 2,296 feet of quay and a capacity of roughly 800,000 TEUs annually. In the next two to three years another 984 feet of quay will be added so that two neo-Panamax ships may berth simultaneously. Mariel’s channel, deep enough for Panamaxes at present, will be dredged to neo-Panamax depths by 2017. Over the longer term the terminal will add another 5,577 feet of quay and boost annual capacity to 3 million TEUs. There are also plans to add general cargo, dry bulk and roll-on, roll-off terminals to the port.
Much hinges on Mariel’s location in Cuba’s far northwest.
Skeptics of the port have argued that this location is unsuitable to transshipment because the east-west services that pass through the Caribbean on their way to the U.S. pass by Cuba’s southeast corner, near Guantanamo Bay. They believe the additional transit time to Mariel would be too great.
Baker, however, believes that Mariel can use its location to its advantage.
He said Mariel aims to be the first port of call for neo-Panamax container ships after passing through the Panama Canal to the U.S. East Coast, with feeder services providing direct connections from Mariel to Gulf Coast ports in Tampa, Florida; Mobile, Alabama; New Orleans, Louisiana; Houston, Texas and Altamira, Mexico.
“It will be a challenge to attract the bigger vessels (that will serve the region after Panama Canal expansion) to circle into the U.S. Gulf, because there would not be enough time in their schedules,” he said, explaining why carriers would prefer to use a hub to serve Gulf ports. Dropping cargo off in Mariel and feedering it to Gulf ports would also be more attractive to shippers, given “vastly improved” transit times, he said. “Today, to ship to Mobile, you’ll have to wait for the vessel to sail in and out of Houston and New Orleans before it gets there.
“When we talk to the carriers and the ports, they do recognize (the benefits of) our geography, but they also recognize very clearly that the U.S. embargo stands in the way of the opportunity we have here,” he said.
Although the embargo is the biggest hurdle to Mariel increasing its transshipment business, another issue is current U.S. law, which dictates that a vessel regardless of flag cannot call at a U.S. port within 180 days of calling in Cuba. This effectively prevents transshipment from Mariel because any vessel deployed for feedering would lose the flexibility to call in the United States for an extended period, and more importantly, mainline vessels cannot sail to final destinations in the United States after dropping off transshipment cargo (bound for non-U.S. destinations) in Mariel.
A repeal of that 180-day rule would be “tremendous” for TC Mariel, Baker said. “It would allow us to enter the international transshipment market.” Baker recently traveled to Washington, D.C., to meet with Congressional staffers and push for an end to the rule.
TC Mariel also benefits from its location within the enormous Special Development Zone of Mariel, or ZED Mariel. “This zone is very, very important and very high on the agenda for the Cuban government,” said Baker. “It has a special set of laws and regulations that are very advantageous to investors and it is the first part of Cuba that allows 100 percent foreign ownership. It is 465 square kilometers (180 square miles) in size, which is half the landmass of Singapore. It is probably the largest greenfield industrial development zone in the world — and it really is green. There is literally nothing there today,” he said, noting how rare it is to have a major port adjacent to a huge expanse where logistics, assembly, industrial and warehousing facilities can be developed without space restrictions.
Interest in ZED Mariel continues to grow and more investments are being made.
“There is a lot of European interest now because they have realized that if the embargo disappears, they will be facing intense pressure in a market where they’ve been well protected from U.S. exporters for the last 54 years,” said Baker. “Some of them are realizing that the way to maintain their market share is to plant themselves in Cuba (before the end of the embargo). They also realize that going forward, there will be a wonderful opportunity to export to the world’s largest consumer market, only 90 miles away.”\