by Nancy Macdonald and Gabriela Perdomo
Original Article is located here: Maclean’s Magazine, August 8, 2012
Until this spring, Stephen Purvis had it all. The British architect, who’d helped launch the Saratoga, Cuba’s poshest hotel, was one of the more prominent figures in Havana’s business community. As chief operating officer of Coral Capital, one of Cuba’s biggest private investors, he was overseeing a planned $500-million resort in the sleepy fishing village of Guanabo. The Bellomonte resort, which would allow foreigners to buy Cuban property for the first time, was part of Havana’s ambitious, multi-billion-dollar plan to attract high-end tourists and badly needed foreign exchange. Everything he touched seemed to turn to gold. The musical Purvis produced in his spare time, Havana Rakatan, had a run at the Sydney Opera House last year before moving on to London’s West End. But in April, the 51-year-old was arrested on suspicion of corruption as he prepared to walk his kids to school in Havana.
Purvis’s arrest could have been anticipated. Coral Capital’s British-born CEO, Amado Fakhre, has been held without charges ever since his arrest in a dawn raid last fall. The investment firm is being liquidated, and both men have faced questioning at Villa Marista, Cuba’s notorious counter-intelligence headquarters. They are not alone. Since last summer, dozens of senior Cuban managers and foreign executives, including two Canadians, have been jailed in an investigation that has shocked and terrified foreigners who do business in the country.
Since replacing his brother Fidel as president in 2008, Raúl Castro has painted himself as a reformer, and Cuba as a place where foreign businesses can thrive. Over the last year, he has relaxed property rights, expanded land leases and licensed a broad, if random, list of businesses—everything from pizza joints to private gyms. And he’s endorsed joint venture golf courses, marinas and new manufacturing projects. Canadians are chief among those heeding Raúl’s call to do business with Havana. Hundreds have expressed interest in the Cuban market in the last year alone, according to Canada’s Trade Commissioner Service. Flattering reports in Canadian media have praised Raúl’s efforts. Yet they seem to overlook troubling signs that Cuba appears to be moving backwards.
Raúl’s sweeping changes were meant to pave the way for massive foreign investment in Cuba. The country, which was forced to lay off 20 per cent of its public workforce last year, is barely as developed as Haiti, and will need an influx of foreign cash to stay afloat. There is urgency to the project. Time is running out for Venezuelan President Hugo Chávez, Cuba’s benefactor, who funds the country to the tune of $10 billion a year, says José Azel, a University of Miami research associate. At home, Chávez, who is sick with cancer, is also fighting off a tough challenge from Henrique Capriles in presidential elections slated for October. His successor will almost certainly cut Cuba’s generous aid package to deal with Venezuela’s own needs.
So a strange incongruity exists in Cuba today: Havana is bending over backwards to attract foreign currency at the same time it is imprisoning some of its biggest Western investors. For all Cuba’s reforms, this Castro appears to be as intent on maintaining an iron grip on the country as the last one.
Few are more keenly aware of the pitfalls of doing business in the new Cuba as a pair of Canadians sitting in jail in Havana. It has been more than a year since Sarkis Yacoubian, the president of Tri-Star Caribbean, a trading firm with headquarters in Nova Scotia, was detained in the Cuban capital. And September will be the one-year anniversary of the arrest of Cy Tokmakjian, the president of a trading company based in Concord, Ont. He and Yacoubian have both been imprisoned without charges. Their assets now belong to Cuba. No trial date has been announced.
Both Yacoubian and Tokmakjian ran well-established businesses in Cuba, had years of experience in the country, and multi-million-dollar contracts with several government ministries. Yacoubian imported the presidential fleet of BMWs. Tokmakjian, who’d been in Cuba for more than 20 years and did $80 million in annual business there, had the rights to Hyundai and Suzuki, which are used by the country’s police.
So far, Raúl has scared off more joint ventures than he has attracted, jeopardizing the investment Cuba needs to succeed. Spanish oil giant Repsol quit the country in May. Canada’s Pizza Nova, which had six Cuban locations, packed its bags, as did Telecom Italia. The country’s biggest citrus exporter, BM Group, backed by Israeli investors, is gone. A Chilean who set up one of Cuba’s first joint enterprises, a fruit juice company, fled after being charged with corruption last year. He was convicted in absentia. Shipping investors are pulling out, even as Cuba prepares to open a new terminal on the island’s north coast.
Experts say Raúl’s crackdown is an attempt to reassert control. By targeting the biggest names in the business community, he’s sending a message, says Azel. “Raúl doesn’t want to be Gorbachev,” the Soviet statesman who brought down Communism in the former Soviet Union. “He wants to be the guy who makes socialism work.”
Yet as detentions pile up it remains unclear what exactly the jailed Canadians and Britons have done, or what the regime means by clamping down on corruption. “Cuba’s version of what is legal and proper is different from the rest of the world,” says Ted Henken, president of the Washington-based Association for the Study of the Cuban Economy. Even sales commissions are viewed as corrupt, says Yoani Sánchez, a Havana-based journalist. Foreign companies can’t pay their Cuban employees any more than the standard wage, about $20 a month, says Sánchez—barely enough for two weeks’ living in poor conditions with a poor diet. Many foreign bosses routinely top up pay with bonuses and commissions, which Havana considers bribery. For years, says Henken, corruption was the grease that made wheels turns. “You got what you needed to live from what was thrown off the back of the truck.”
It is not clear whether the detained Canadians are facing charges for salary top-ups, for example, or for legitimate corruption allegations. Canada’s Foreign Affairs department would only confirm that “consular services are being provided to two Canadian citizens detained in Cuba.” Executives at Tri-Star Caribbean and members of the Tokmakjian family declined comment, citing the “extremely sensitive” nature of the situation.
Azel’s advice to potential Canadian investors? Stay away. “You’re defenceless. There’s no independent judiciary to adjudicate any kind of claim,” he says. “Doing business with Cuba is a very risky proposition.”
So then why all the new resorts and planned golf courses? Why do so many Brits and Canadians take the personal and business risk? Because it’s widely believed that the days are numbered for the U.S. travel ban on Cuba, which has barred Americans from visiting the island for almost three decades. Predictions for tourism growth are off the charts—up to six million annual visitors, from two million today, says Gregory Biniowsky, a Canadian consultant who’s lived in Cuba for two decades. Cuba’s boosters believe the country, with its vast, undeveloped white sand beaches, just 45 minutes by plane from Florida, could come to rival Jamaica or the Dominican Republic as a tourist draw. “It’s just a matter of time before things boom here,” says Biniowsky. Five billion barrels of oil lie under Cuba’s waters, according to the U.S. Geological Survey. To some, getting in on the ground floor is worth the risk. But foreign investors who lose sight of the dangers could find themselves in serious trouble.
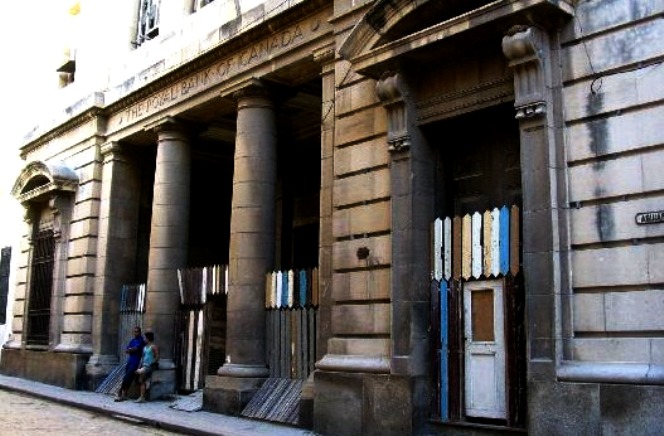 The old Royal Bank of Canada Building in Havana. The interior of the building is below.
The old Royal Bank of Canada Building in Havana. The interior of the building is below.
Photos by Arch Ritter, April 2012