Attached is a Power Point Presentation delivered at Kennesaw State University on October 24, 2019. Kennesaw Presentation on Cuban Economy, October 24, 2019
Attached is a Power Point Presentation delivered at Kennesaw State University on October 24, 2019. Kennesaw Presentation on Cuban Economy, October 24, 2019
Attached is the PDF of a P.Pt. presentation delivered at Kennesaw State University on October 24, 2019 entitled Public and Private, Market and Plan:Some Lessons from Cuba and the United State:
Carmelo Mesa-Lago, Catedrático de servicio distinguido emérito en Economía y Estudios Latinoamericanos en la Universidad de Pittsburgh
Pavel Vidal Alejandro, Profesor asociado del Departamento de Economía de la Universidad Javeriana Cali, Colombia
30 de mayo de 2019
Índice
Resumen, Abstract……………………………………………………………………………………….. 2
Introducción ………………………………………………………………………………………………… 3
(1) Antecedentes de la relación económica entre ambos países …………………………. 4
(2) Análisis de la severidad de la crisis económica-social venezolana ……………….. 5
(3) Evolución del comercio exterior cubano con Venezuela……………………………….. 7
(4) Las medidas de Trump contra Venezuela y Cuba ……………………………………….. 14
(5) Los efectos del shock venezolano ……………………………………………………………….. 18
(6) ¿Viene otro Período Especial? …………………………………………………………………….. 22
(7) Posibilidad de que otros países (Rusia o China) sustituyan a Venezuela ……….. 23
(8) ¿Hay alternativas viables para Cuba? ………………………………………………………… 24
(9) Conclusiones……………………………………………………………………………………………… 30
Históricamente, Cuba ha padecido la dependencia económica de otros países, un hecho que continúa después de 60 años de la revolución. La dependencia con la Unión Soviética en 1960-1990 dio lugar al mejor período económico-social en la segunda mitad de los años 80, pero la desaparición del campo socialista fue seguida en los años 90 por la peor crisis desde la Gran Depresión. Este documento de trabajo analiza de manera profunda la dependencia económica cubana de Venezuela en el período 2000- 2019: (1) antecedentes de la relación económica entre ambos países; (2) análisis de la severidad de la crisis venezolana; (3) evolución del comercio exterior cubano con Venezuela; (4) medidas de Donald Trump contra Venezuela y Cuba; (5) efectos del shock venezolano en Cuba; (6) ¿viene otro Período Especial en Cuba?; (7) posibilidad de que otros países (Rusia o China) substituyan a Venezuela; y (8) alternativas viables a la situación. El impacto en la economía cubana de la crisis venezolana y de las políticas de Donald Trump
Cuba has historically endured an economic dependence on other nations that continues after 60 years of revolution. Dependence on the Soviet Union in 1960-90 led to its best economic and social situation in the second half of the 1980s, but the disappearance of the socialist world was followed in the 1990s by its worst economic crisis since the Great Depression. This Working Paper analyses Cuba’s economic dependence on Venezuela in 2000-19, as follows: (1) antecedents of the economic relationship between the two countries; (2) evaluation of the severity of Venezuela’s economic-social crisis; (3) evolution of Cuba’s trade relationship with Venezuela; (4) Trump’s measures against Venezuela and Cuba; (5) effects of the Venezuelan shock on Cuba; (6) is another Special Period in the offing?; (7) possibility of another country (Russia or China) replacing Venezuela; and (8) viable alternatives to Cuba.
…………………………………………..
Conclusiones
Este estudio ha aportado evidencia abundante y sólida (respecto a Venezuela) que ratifica la histórica dependencia económica cubana de otra nación y la necesidad de subsidios y ayuda sustanciales para poder subsistir económicamente.
A pesar del gran peso de la beneficiosa relación económica externa, Cuba no ha logrado financiar sus importaciones con sus propias exportaciones. La ayuda externa resulta, al menos por un tiempo, en un crecimiento económico adecuado (en 1985-1989 con la URSS y en 2005-2007 con Venezuela), pero cuando desaparece o entra en crisis el país subsidiador, ocurre una grave crisis en Cuba. La dependencia sobre Venezuela ha sido menor que la relativa con la Unión Soviética y hay además otros factores que podrían atenuar la crisis resultante de la debacle en el primer país; aun así, Cuba ya ha sufrido
El impacto en la economía cubana de la crisis venezolana y de las políticas de Donald Trump Documento de trabajo 9/2019 – 30 de mayo de 2019 – Real Instituto Elcano 31 desde 2012 una pérdida equivalente al 8% de su PIB y una caída del régimen de Maduro agregaría otro 8%. Las medidas de Trump contra Venezuela no han conseguido hasta ahora derrocar el régimen de Maduro y este ha logrado circunscribir algunas de ellas, pero han agravado la crisis en la República Bolivariana creado una situación peliaguda que se agravará en el medio y largo plazo.
Por otra parte, las políticas trumpistas contra Cuba probablemente tendrán un impacto adverso sobre las remesas externas y el turismo (respectivamente la segunda y tercera fuentes de divisas cubanas), mientras que la aplicación del título III de la ley Helms-Burton generaría costes considerables por las demandas interpuestas y un efecto de congelamiento en la inversión futura.
La reacción de la dirigencia cubana frente a la crisis que se agrava ha sido el continuismo, de lo que no ha funcionado por seis décadas; muy poco se dice oficialmente (aunque se destaca por los académicos economistas del patio) sobre la urgente y necesaria profundización de las reformas económicas fallidas de Raúl Castro, a fin de adoptar algunas de las políticas del socialismo de mercado practicado con éxito en China y Vietnam. Para que Cuba pueda encarar la dura crisis que se avecina a corto plazo y conseguir escapar de la dependencia económica externa a largo plazo, esa es la alternativa más viable.
Boulder, CO: First Forum Press, 2015. 373 pp.
By Archibald R. M. Ritter and Ted A. Henken
Review by Sergio Díaz-Briquets,
Cuban Studies, Volume 46, 2018, pp. 375-377, University of Pittsburgh Press
 The small business sector, under many different guises, often has been, since the 1960s, at the center of Cuban economic policy. In some ways, it has been the canary in the mine. As ideological winds have shifted and economic conditions changed, it has been repressed or encouraged, morphed and gone underground, surviving, if not thriving, as part of the second or underground economy. Along the way, it has helped satisfy consumer needs not fulfilled by the inefficient state economy. This intricate, at times even colorful, trajectory has seen the 1968 Revolutionary Offensive that did away with even the smallest private businesses, modest efforts to legalize self-employment in the 1979s, the Mercados Libres Campesinos experiment of the 1980s, and the late 1980s ideological retrenchment associated with the late 1980s Rectification Process.
The small business sector, under many different guises, often has been, since the 1960s, at the center of Cuban economic policy. In some ways, it has been the canary in the mine. As ideological winds have shifted and economic conditions changed, it has been repressed or encouraged, morphed and gone underground, surviving, if not thriving, as part of the second or underground economy. Along the way, it has helped satisfy consumer needs not fulfilled by the inefficient state economy. This intricate, at times even colorful, trajectory has seen the 1968 Revolutionary Offensive that did away with even the smallest private businesses, modest efforts to legalize self-employment in the 1979s, the Mercados Libres Campesinos experiment of the 1980s, and the late 1980s ideological retrenchment associated with the late 1980s Rectification Process.
Of much consequence—ideologically and increasingly economically—are the policy decisions implemented since the 1990s by the regime, under the leadership of both Castro brothers. Initially as part of Special Period, various emergency measures were introduced to allow Cuba to cope with the economic crisis precipitated by the collapse of the communist bloc and the end of Soviet subsidies. These early, modest entrepreneurial openings were eventually expanded as part of the deeper institutional reforms implemented by Raúl upon assuming power in 2006, at first temporarily, and then permanently upon the resignation of his brother as head of the Cuban government.
In keeping with the historical zigzag policy pattern surrounding small businesses activities—euphemistically labeled these days as the “non-state sector”—while increasingly liberal, they have not been immune to temporary reversals. Among the more significant reforms were the approval of an increasing number of self-employment occupations, gradual expansion of the number of patrons restaurants could serve (as dictated by the allowed number of chairs in privately owned paladares), and the gradual, if uneven, relaxation of regulatory, taxing, and employment regulations. Absent has been the authorization for professionals (with minor exceptions, such as student tutoring) to privately engage in their crafts and the inability to provide wholesale markets where self-employed workers could purchase inputs for their small enterprises.
The authors of this volume, an economist and a sociologist, have combined their talents and carefully documented this ever-changing policy landscape, including the cooperative sector. They have centered their attention on post–Special Period policies and their implications, specifically to “evaluate the effects of these policy changes in terms of the generation of productive employment in the non-state sector, the efficient provision of goods and services by this emergent sector, and the reduction in the size and scope of the underground economy” (297).
While assessing post-1990 changes, Entrepreneurial Cuba also generated a systematic examination of the evolution of the self-employment sector in the early decades of the revolution in light of shifting ideological, political, and economic motivations. Likewise, the contextual setting is enhanced by placing Cuban self-employment within the broader global informal economy framework, particularly in Latin America, and by assessing the overall features of the second economy in socialist economies “neither regulated by the state nor included in its central plan” (41). These historical and contextual factors are of prime importance in assessing the promise and potential pitfalls the small enterprise sector confronts in a changing Cuba.
Rich in its analysis, the book is balanced and comprehensive. It is wide ranging in that it carefully evaluates the many factors impinging on the performance of the small business sector, including their legal and regulatory underpinnings. The authors also evaluate challenges in the Cuban economic model and how they have shaped the proclivity for Cuban entrepreneurs to bend the rules. Present is a treatment of the informal social and trading networks that have sustained the second economy, including the ever-present pilfering of state property and the regulatory and transactional corruption so prevalent in Cuba’s centralized economy.
While none of the above is new to students of the Cuban economy—as documented in previous studies and in countless anecdotal reports—Ritter and Henken make two major contributions. First, they summarize and analyze in a single source a vast amount of historical and contemporary information. The value of the multidisciplinary approach is most evident in the authors’ assessment of how the evolving policy environment has influenced the growth of paladares, the most important and visible segment of the nonstate sector. By focusing on this segment, the authors validate and strengthen their conclusions by drawing from experiences documented in longitudinal, qualitative case studies. The latter provide insights not readily gleaned from documentary and statistical sources by grounding the analysis in realistic appreciations of the challenges and opportunities faced by entrepreneurial Cubans. Most impressive is the capacity of Cuban entrepreneurs to adapt to a policy regime constantly shifting between encouraging and constraining their activities.
Commendable, too, is the authors’ balanced approach regarding the Cuban political environment and how it relates to the non-state sector. Without being bombastic, they are critical of the government when they need to be. One of their analytical premises is that the “growth of private employment and income represents a latent political threat to state power since it erodes the ideals of state ownership of the means of production, the central plan, and especially universal state employment” (275).
This dilemma dominates the concluding discussion of future policy options. Three scenarios are considered possible. The first entails a policy reversal with a return to Fidel’s orthodoxy. This scenario is regarded as unlikely, as Raúl’s policy discourse has discredited this option. A second scenario consists of maintaining the current course while allowing for the gradual but managed growth of the non-state sector. While this might be a viable alternative, it will have limited economic and employment generation effects unless the reform process is deepened by, for example, further liberalizing the tax and regulatory regimes and allowing for the provision of professional services.
The final scenario would be one in which reforms are accelerated, not only allowing for small business growth but also capable of accommodating the emergence of medium and large enterprises in a context where public, private, and cooperative sectors coexist (311). As Ritter and Henken recognize, this scenario is unlikely to come to fruition under the historical revolutionary leadership, it would have to entail the resolution of political antagonisms between Washington and Havana, and a reappraisal by the Cuban government of its relationship with the émigré population. Not mentioned by Ritter and Henken is that eventual political developments—not foreseen today—may facilitate the changes they anticipate under their third scenario.
In short, Entrepreneurial Cuba is a must-read for those interested in the country’s current situation. Its publication is timely not only for what it reveals regarding the country’s economic, social, and political situation but also for its insights regarding the country’s future evolution.
…………………………………………………………………………….
Table of Contents,
List of Charts and Figures
Chapter I Introduction
Chapter II Cuba’s Small Enterprise Sector in International and Theoretical Perspective
Chapter III Revolutionary Trajectories, Strategic Shifts, and Small Enterprise, 1959-1989
Chapter IV Emergence and Containment During the “Special Period”, 1990-2006
Chapter V The 2006-2011 Policy Framework for Small Enterprise under the Presidency of Raul Castro
Chapter VI The Movement towards Non-Agricultural Cooperatives
Chapter VII The Underground Economy and Economic Illegalities
Chapter VIII Ethnographic Case Studies of Microenterprise, 2001 vs. 2011
Chapter IX Summary and Conclusions
APPENDIX
GLOSSARY
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Carmelo Mesa-Lago, University of Pittsburgh,
Latin American Research Review, July 2017 https://doi.org/10.25222/larr.2
This essay reviews the following works:
Open for Business: Building the New Cuban Economy. By Richard E. Feinberg. Washington DC: Brookings Institution Press, 2016. Pp. vii + 264. $22.00 cloth. ISBN: 9780815727675.
Miradas a la economía cubana: Análisis del sector no estatal. Edited by Omar Everleny Pérez Villanueva and Ricardo Torres. La Habana: Editorial Caminos, 2015. Pp. 163. $5, paper. ISBN: 9789593031080.
Entrepreneurial Cuba: The Changing Policy Landscape. By Archibald R. M. Ritter and Ted A. Henken. Boulder, CO: First Forum Press, 2015. Pp. xiv + 374. $79.95 cloth. ISBN: 9781626371637.
Retos para la equidad social en el proceso de actualización del modelo económico cubano. Edited by María del Carmen Zavala et al. La Habana: Editorial Ciencias Sociales, 2015. Pp. vi + 362. $20 paper. ISBN: 9789590616105.
Soon after current president of the State Council Raúl Castro took over power in Cuba from his brother Fidel in 2006, he started structural reforms to cope with the serious socioeconomic problems accumulated in the previous forty-five years. Some authors, including a few in this review, argue that Cuba is in transition to a mixed economy. Despite the importance of these changes, however, the official view is that central planning will predominate over the market, and state property over private property.1 A main reform goal was to fire 1.8 million unneeded workers in the state sector, which demanded an expansion of the “non-state sector” (NSS) to provide jobs to those dismissed. The four books I review are commendable additions to the growing literature on the NSS (inside and outside Cuba), as they fill some of its existing gaps, to be identified below.2 A few authors rely on surveys to gather data, but surveys are not easy to take in Cuba; hence the majority used interviews of different size and representativeness, as well as in-depth conversations.
Within the NSS, the most dynamic four groups are self-employed workers (507,342), usufruct farmers (312,296), and members of new nonagricultural and service co-ops, NASCs (only 7,700 so far). Altogether these make up 17 percent of the labor force, out of a total 29 percent in the entire NSS.3 Except for the most recent NASCs, the other three forms were legalized during the severe crisis of the 1990s but did not take off until much later. Selling and buying of private dwellings, banned in 1960 and reauthorized in 2011, involve at least 200,000 transactions but still only 5 percent of the total housing stock. The books reviewed in this essay mainly concentrate on self-employment and to a much lesser extent on NASCs.
The main gaps treated by the books are the NSS’s history; size and personal profiles; relations with the state; progress achieved and obstacles faced; the role of variables—age, gender (most treated), race, education, and location—on growing inequalities; particular issues such as access to raw materials, capital and credit, competition, and taxes; and NSS perspectives. This review discusses the data, method, and evidence that each researcher uses and the major issues and findings, arguing that the size of the NSS remains questionable.
In Entrepreneurial Cuba, Archibald Ritter and Ted Henken combine their economic and sociological expertise to produce an encyclopedic, balanced, and laudable volume on the development of the NSS in Cuba. Targeted on self-employment and, to a lesser extent, on NASCs, the book also tackles broader topics like the “underground” economy. It starts with an examination of small enterprises in general, internationally, and its lessons for Cuba. Based on historical and comparative approaches, Ritter and Henken discuss the evolution of self-employment throughout Cuban contemporary history. In the socialist period, they compare Cuban policies with those of the USSR and Eastern Europe; furthermore they contrast Fidel’s hostility to the NSS (except for reluctant support in times of economic crisis) with Raúl’s more pragmatic and positive style, which does not exempt the sector from tight controls, restrictions, and taxes. Largely based on my cycles approach,4 the history of self-employment under socialism is divided in three periods (each one covered in a chapter): 1959–1990, trajectories and strategic shifts; 1990–2006, the “Special Period”; and 2006–2014, Raúl’s reforms.
Ritter and Henken conclude that the NSS has grown and achieved substantial progress: for instance, increase in authorized activities and licenses, broadened legal markets, deduction of part of the expenses for tax purposes, micro credits and banking facilities, and rental of state facilities. Conversely they identify limitations, like narrow definition of legal activities, exclusion of most professional and high-tech occupations, multiple taxes and taxation at a high level, lack of wholesale markets, bureaucratic resistance, obstacles to hiring employees, and discrimination in favor of foreign firms. They provide suggestions to overcome these problems. Lack of space impedes a more profound treatment of this book, the most comprehensive and profound on self-employment so far. The structure of the book, combining historical stages and current analysis of self-employment and NASC, however, is somewhat complex and leads to a certain overlapping.
Ritter and Henken rely on three series of interviews conducted in Cuba with sixty self-employed workers in 1999–2001, half of them re-interviewed in follow-up visits in 2002 and 2009 and, finally, some revisited in April 2011 to evaluate the impact of Raúl’s reforms. The authors select the three most dynamic, lucrative, and sizeable private activities: small restaurants (paladares), taxis, and lodging. They asked their informants about three issues: (1) ambitions and expectations for the future (whether they expected to become true small- and medium-sized enterprises—SME—in the long run); (2) survival strategies in negotiating with the state (how they responded to the government regulations, licenses, and taxes); and (3) distinctions between licensed and clandestine self-employed workers.
Accompanying abundant evidence, deep analysis, statistical tables, synoptic charts, figures, and useful appendices (including a list of the 201 authorized activities for the self-employed and a timetable of the evolution of NSS in 1959–2014), the authors intersperse vignettes that allow the reader to better understand the daily life of the self-employed. Occasional jewels in the book brighten our knowledge, such as uncovering in fascinating detail the bureaucratic shutdown of El Cabildo, which was the most prosperous private, medium-sized business in Cuba.
Miradas a la economía cubana, a collection edited by well-known Cuban economists Omar Everleny Pérez Villanueva and Ricardo Torres, includes twelve essays that offer a first-rate sample of scholarship on the NSS at the Center for the Study of the Cuban Economy, the best economic think tank in Cuba. The anthology, an excellent complement to the Ritter and Henken book, includes self-employment and NASCs. In the prologue, Juan Valdés Pérez notes that “the new economic model in Cuba is moving [transita] toward a mixed economy, based on a public sector, a mix-capital sector, and a private sector, mostly SME” (14). Most contributors to the volume propose reasonable policies to help the consolidation and further expansion of the NSS.
In the opening chapter, Torres discusses the role of the private sector in a centrally planned economy such as Cuba, which generates an intrinsic conflict. Despite NSS advances, the government still sees it as a supplement to the state sector and imposes clear limits. Hence the NSS role is and will continue to be very minor, if currents trends hold. An important point, among many discussed by Torres, is that its productivity is low, despite the very highly educated labor force (ranked at the top of Latin America), and shows a declining trend due to the low skills of the activities approved. He ends by suggesting, “In a scenario [Cuba] where public enterprises are predominant and mostly inefficient, wealth is not socialized and man is not liberated from alienation, just the opposite” (25). Torres believes that the solution to all existing problems is neither privatization of all public assets nor to insist on old formulas overcome by time, and urges a serious national social debate on these issues.
Pérez Villanueva analyzes and defines self-employment and SME, tracing their evolution and identifying needs such as autonomy, a wholesale market with competitive prices, facilitation of payments through the national banks, and use of highly skilled personnel; he also notes adverse effects like social inequalities (see Zavala et al., below). At the end of his chapter, he asserts that “the Cuban SME would be more viable than the actualization of our economic model and contribute more positive results, providing that the government understands its role and potential” (35).
Camila Piñeiro provides the most comprehensive and deep analysis of NASCs so far. These cooperatives grew 74 percent, from 198 to 345, in 2013–2014, but their tempo slowed to 6 percent in 2015.5 Based on diagnosis and audits done on sixty NASCs in 2014, Piñeiro identifies their achievements (increase in income and motivation, improvement in the locale and working conditions) and problems (complex and delayed creation, insufficient training, and lack of a wholesale market). The most successful NASCs are those created by the voluntary initiative of a group of persons that share the same goals and values (23 percent of all NASCs), and the least successful are those coming from former state enterprises, without negotiating with their workers so that they accept what is decided from above (77 percent).
Mariuska Sarduy, Saira Pons, and Maday Traba analyze tax evasion and underdeclaration of income among self-employed owners. They report that evasion was 12 percent of total fiscal revenue and 60 percent of registered self-employed contributors in 2013–2014. They carried out 300 interviews with self-employed workers in Havana in 2014 and found that 55 percent omitted income in their declaration for the following reasons: 95 percent due to very high taxes; 77 percent blamed the complex procedure to pay taxes; 80 percent knew that evasion or underdeclaration are toughly penalized crimes, but half believed that they were necessary to survive, and 20 percent thought that it was improbable that fiscal authorities would catch them.
Expanding her substantial work on geographic inequalities, Luisa Íñiguez uses the 2012 population census to explore the distribution of NSS enterprises in Cuban provinces and municipalities and shows their differences and contribution to social inequalities. She develops various maps of the island, displaying the location of total NSS enterprises, as well as key components such as the self-employed, usufruct farmers, and small private farmers. In addition, she calculates percentages of components of the NSS relative to the employed labor force. The NSS developed much further after 2012, but her work remains valuable and sets a solid foundation for future study.
The role of women in microenterprises is examined by Ileana Díaz and Dayma Echevarría, relying on data from the 2012 population census and Ministry of Labor and Social Security in 2013, and a survey of thirty-five self-employed owners in Havana circa 2014 (63 percent women and 37 percent men). Among other gender inequalities, they find that women are more hurt than men by the lack of a state policy to foster microenterprises, and by poor access to credit as well as to legal and accounting advice. Interviewees answered key questions with a fair consensus: 50 percent noted unfair competition from state and mixed enterprises; most preferred to work as self-employed instead of for the state; public or private financing was judged insufficient; elementary-secondary school didn’t help in their activity but university did; and they noted poor access to wholesale markets, telecommunications, and vanguard technology. Virtually all interviewees, but a sizably lower percentage of women than men, said that their success was more than expected. Both genders agreed on the major obstacles: limited demand, excessive state bureaucracy and regulations, too much competition, absence of a wholesale market, and difficulties to get inputs.
Retos para la equidad social, edited by Maria del Carmen Zavala et al., contains twenty contributions, all but one authored by women, focused on socioeconomic inequality under Raúl’s structural reforms. Three chapters of the book deal with expanding inequalities among the self-employed by age, gender, race, education, and location, and also with their motivation, satisfaction, competition, capital access, obstacles faced, and views of the future.
The best chapter in the collection, by Daybel Pañellas, Jorge Torralbas, and Claudia Caballero, relies on a survey taken between October 2013 and March 2014 among 419 persons self-employed in fifty-seven activities and located in three districts of Old Havana. They find that age, gender, education, and location are important factors in the quality of occupation, access to capital, and earnings of the self-employed. In the sample, 76 percent worked by themselves, without employees; 13 percent were employers and 11 percent employees; 64 percent were men and 36 percent women; 48 percent were white and 52 percent nonwhite; 54 percent were middle-aged adults, 30 percent young people, and 15 percent elderly; 54 percent had precollege or university education, 31 percent had a low level of education, and 15 percent had a technical education (a highly trained labor force and NSS, also noted by Torres). Not only are women underrepresented, but their activities reproduced their roles in domestic life, such as work in cafeterias, food preparation, manicure, makeup, and as seamstresses. While women rented rooms mostly in national pesos (CUP), men rented rooms in the more advantageous convertible pesos (CUC = 24 CUP). Combining education, race, and gender, the best-educated white males had better occupations than the lowest trained nonwhite females (e.g., computer programing vis-à-vis seamstress). The self-employed were mainly attracted by these features of self-employment (not exclusive categories): better income (80 percent), easier labor journey (20 percent), and being their own bosses (15 percent). Their level of satisfaction ranged from so-so (53 percent), to good/very good (38 percent), to bad/very bad (9 percent)—the higher the educational level the more occupational satisfaction.6 Success in competition was attributed to the quality of product or service (56 percent), business location (24 percent), and low prices (14 percent). Access to capital was mostly by employers that receive remittances, are white, and have higher or middle education, ample social networks, and good locations; conversely, investment is minimal among low-educated nonwhites. Obstacles encountered by the self-employed were lack of access to raw materials (49 percent), heavy taxes (44 percent), lack of financing (35 percent), state control and inspections (33 percent), and legal procedures (23 percent). These proportions varied in the three districts and were influenced by gender, race, and type of activity; for example, controls and inspections were mostly mentioned by workers with low education, nonwhites, and women. On their perceptions for the future, 81 percent believed that the self-employed would prosper—especially if the mentality of the state and the self-employed changes— and 10 percent didn’t think so.
Geydis Fundora expands on the growing inequalities enumerated above, based on a study of fifty-two self-employed residents of Havana Province in 2010–2013, reaching similar conclusions. Out of the 201 activities approved, 65 percent have a male profile; paladar owners mostly hire women because of their sex appeal to clients and because the work is similar to that done at home; other activities are in practice barred to the “weak sex.” Men tend to be employers and women employees, thus resulting in lower decision making and income for women. The elderly are disadvantaged because most activities require physical strength; most young people are hired as employees and in less specialized activities. There is no political will to gather statistics on race, but whites predominate over blacks and mulattoes, opposite to what Pañellas, Torralbas, and Caballero found; nonwhites have less access to capital and hence to success and higher earnings. Those that have a high initial capital—coming from savings, remittances, or hidden foreign investment—enjoy an advantage over the rest not only to establish the business but also to buy inputs, pay taxes, and bribe inspectors. Location in more attractive and populous zones are keys to success.
Magela Romero targets self-employed women engaged on infant care, a most-needed occupation to increase female participation in the employed labor force, which was 37 percent of the total in 2015;7 the low proportion is an outcome of resilient traditional gender roles at home and work. Based on eighteen cases in the town of Cojímar (in Havana) in 2013, the study found that all those self-employed in infant care were women, and half of them had previously been informal domestic employees. All said that their main attraction was a higher income, but all also complained of exhausting work and high responsibility with a monthly salary of 200 CUP per infant, with a maximum of five infants, equal to US$40, still three times the mean average salary in the state sector.
Open for Business by Richard E. Feinberg deals mainly with the economic events following the process of normalization between the United States and Cuba that started at the end of 2014, preceded by a summary of the previous state of the Cuban economy and Raúl’s reforms. Feinberg believes that the emerging NSS “offers the best hope for a more dynamic and efficient Cuban economy, especially if it is permitted to partner with foreign investment and with more efficient state-owned enterprises” (132). One chapter on emerging entrepreneurs is based on a monograph he published in 2013, which at that time provided substantial data and analysis on self-employment, preceding the other three books reviewed herein.8 One graph and one table are updated to mid-2015, but most of the text remains unchanged. The author and an assistant had in-depth conversations with twenty-five microentrepreneurs between March 2012 and April 2013, emphasizing financial issues (averages of time open, number of employees, starting capital, and use of domestic and foreign capital). Interesting profiles of self-employed activities are given on paladares, cafeterias and catering, bed and breakfasts, accounting, a shop selling handicrafts to tourists, building construction and house remodeling, electronic repairs, and renting of 1950s cars; from such profiles he extracts useful lessons.9 A stimulating innovation is the selection of twelve young Cuban “millennials” (aged 20–35), one of them the owner of a cafeteria, for appealing interviews based on ten questions.
Feinberg envisages four stages of capital accumulation of microbusinesses: primitive household accumulation, early-mover super-profits, growth and diversification, and strategic alliances with state enterprises and with foreign investors (not yet authorized). Like the other authors whose books I review here, he stresses the progress and achievements of self-employment, perhaps more so than other authors. But he also pinpoints the many constraints the self-employed face: poor banking and meager credit, serious scarcity of inputs of all sorts (as a visible exception he gives the wholesale market “El Trigal,” temporarily closed in May 2016), shortage of commercial rental space, a very challenging business climate, and government restrictions including persecution by government inspectors and heavy fines, as well as constraints on capital accumulation and business growth. He provides his own recommendations to alleviate these problems.
One fundamental question left unanswered is the size of the NSS. Unfortunately, there are no official data on the NSS, complete and disaggregated by components. Neither Ritter and Henken nor most Cuban authors provide such a figure (Torres estimates it as 27 percent of the labor force; p. 21). The only elaborated calculation in the four books is Feinberg’s, who states that “altogether, as many as 2 million enterprising Cubans—40 percent of total employment—and possibly even more can be counted within the private sector” and predicts that “in the next three to five years, total private employment could reach 45 to 50 percent of the active labor force” (Feinberg, 132, 139; emphasis added); this exceeds by 10 percentage points Torres’s middle-term estimate of 35 to 40 percent (24).
Feinberg overestimates the NSS’s size. First, an important semantic and substantive issue is that not all NSS participants are private, only most self-employed workers and their employees as well as small private farmers are. Usufruct farmers, NASCs, and other cooperatives’ members do not own their land or buildings; these belong to the state, which leases them to the workers. Second, several figures in Feinberg’s estimates are either questionable or not supported by specific sources; the main query is what he labels “other private activities (estimated),” such as full-time unregistered self-employment and partial self-employment done by state-sector employees, which add up to between 185,000 and 1,185,000, based on guesstimates (while it is true that some government employees work part-time as self-employed workers, it is impossible to know for how many hours, which makes it difficult to estimate average full days of work). Third is the inclusion of 353,000 members of credit and service cooperatives (CCS), because that number exceeds by 65 percent the total number of all co-op members in 2015, including agricultural production (UBPCs, Basic Units of Agricultural Production, and CPAs, Agricultural Production Co-ops), CCSs (Credit and Services Co-ops) and NASCs.10 Furthermore, many private and usufruct farmers are also members of CCSs, thus they are counted twice. Fourth, the category of “land lease farmers” (172,000) is confusing; on the one hand Feinberg does not specifically include usufruct farmers (312,296), and on the other hand the official data on land leasers (arrendatarios) is only 2,843.11 Fifth, employees of self-employed workers are counted since 2011 in the total number of the self-employed, mixed with owners, and we have shown that there is a double counting in the overall figure. In any case, the official statistics on the total NSS share in the employed labor force expanded from 17 percent in 2008, when Raúl officially became president, to 29 percent in 2015.12 In conclusion, there is no doubt that the NSS is important and growing, but certainly not as much as Feinberg estimates.
In summary, the most studied NSS group is the self-employed; NASCs are briefly discussed by Ritter and Henkel and in Piñeiro’s chapter in Zavala et al. Largely excluded from the discussion are usufruct farmers, and totally omitted is the selling/buying of private homes. The historical approach is followed most intensively by Ritter and Henken, although several Cuban authors provide summaries of the evolution in their respective topics. The preferred methodology is interviews or conversations combined with research. There is a consensus that the NSS (mostly self-employment) has been successful despite considerable obstacles. We lack a reliable estimate of the NSS’s size.
Missing in the four volumes is an evaluation of the NSS’s macroeconomic effects.13 Ritter and Henken refer to some results of self-employment, such as job creation, noting the nonfulfillment of the official target of dismissing more than one million unneeded state employees. None of the books discuss the impact of usufruct farming on agricultural output, where NASC members are still minute and their impact is even more difficult to assess. It is true that the scarcity of available data hinder the task, but still some estimation could have been done on the NSS’s effect on produce sales, fiscal revenue, and GDP.14
Feinberg and Ritter and Henken are the only authors who explore the future of the NSS. Feinberg provides three broad overall scenarios, which are thought-provoking but touch little on the NSS: (1) “inertia” with little change, without citing potential precedents and projecting self-employment to 750,000, 48 percent higher than the March 2016 official figure of 507,342; (2) “botched transition and decay,” the most pessimistic, similar to former states of the USSR, but with self-employment expanding to 1 million, twice its 2016 size, as some restraints are removed; and (3) “soft landing” in 2030, the most optimistic, under market socialism as in Vietnam, where self-employment really takes off and reaches 2 million employees and 40 percent of the labor force—this is somewhat confusing because he refers to the private sector and had previously predicted, for the entire NSS, 45 to 50 percent in 2019–2021 (203–222).
Ritter and Henken offer three possible alternative routes for the NSS, without predicting its size: (1) reversal to Fidel’s hostile approach, which they judge very improbable because it is totally unfeasible and discredited (“unlikely to be reversed” for Feinberg, 131); (2) stabilization of Raúl’s current (2014) and cautious reform package to self-employment and NASCs, which would remain in place for the rest of his presidency, but with a significant expansion of both and the potential of creating a “mixed cooperative market economy”; and (3) acceleration of the reform and rebalancing among public, private, and cooperative sectors, with medium and large private enterprises advancing at the expense of co-ops and smaller private enterprises; the viability of this scenario, they say, could be helped by a “serious relaxation of US policy toward Cuba” that could “encourage the Cuban government pro-market openings” (311).
Cuba is always unpredictable, and none of the three scenarios by the above authors completely fit the situation in August 31, 2016, when this review essay was finished. Ritter and Henken’s book was concluded in October 2014, thus this reviewer has the unfair advantage of almost two years that have brought significant changes, such as the evolution of US-Cuba rapprochement in 2014–2016 and the Seventh Congress of the Communist Party held in April 2016.15 In light of those events, their first and third alternatives are implausible, at least in the medium and long run; the second might be conceivable if the emphasis is placed on “stability” instead of significant expansion. By August 2016, however, rapprochement, rather than helping the reforms, appeared to have the opposite effect due to dread in the leadership caused by Obama’s visit and it effects, reflected in the results of the Seventh Party Congress. The number of self-employed workers peaked at 504,613 in May 2015, declined to 496,400 in December, and climbed again to 507,342 in March 2016, an increase of 0.7 percent in ten months, substantially lower that the expansion rate in 2014 and 2015 (14 and 3 percent, respectively). Furthermore, at the Congress, Raúl warned that although NSS forms are not antisocialist, “powerful external forces” try to “empower” them as agents of change, and could risk further “concentration of wealth and property” (the latter was not among the agreements of the Sixth Congress in 2011), making it necessary to impose “well-defined limits” on them.16 The Seventh Congress also recommended to halt the creation of new NASCs because of their deficiencies, and to concentrate on the existing ones instead.17 Finally, the only existing wholesale market was temporarily closed in May 2016. Feinberg’s book ended in early 2016, much later than Ritter and Henken’s, but his scenarios and predictions don’t correlate well with the facts explained above: “inertia” looks optimistic and even more so “decay”—both appear to be short- or middle-term effects—whereas the 2030 “soft landing” would require the drastic changes detailed by him, which are difficult to visualize now.
1 These basic principles of the reforms were set in the Sixth Communist Party Congress of 2011 and ratified in the Seventh Congress of 2016.
2 The pioneer book in the field is Jorge F. Pérez-López, Cuba’s Second Economy: From Behind the Scenes to Center Stage (New Brunswick: Transaction Publishers, 1995).
3 Oficina Nacional de Estadística e Información (ONEI), Anuario Estadístico de Cuba 2015 (La Habana, 2016).
4 Carmelo Mesa-Lago, Market, Socialist, and Mixed Economies: Comparative Policy and Performance; Chile, Cuba, and Costa Rica (Baltimore: John Hopkins University Press, 2000).
5 ONEI, Anuario Estadístico de Cuba 2015.
6 A series of interviews conducted by five authors in 2014–2015, in a much wider part of Havana City, agreed with the predominance of men over women, the highest participation of middle-aged adults, and the important role of education, but found a prevalence of whites and a higher level of satisfaction. Carmelo Mesa-Lago et al., Voces de cambio en el sector no estatal cubano: Cuentapropistas, usufructuarios, socios de cooperativas y compraventa de viviendas (Madrid: Editorial Iberoamericana Vervuert, 2016).
7 ONEI, Anuario Estadístico de Cuba 2015.
8 Richard E. Feinberg, Soft Landing in Cuba? Emerging Entrepreneurs and Middle Classes (Washington, DC: Brookings Institution, 2013).
9 These cases are more varied than those discussed by Ritter and Henken, but the latter provided the most comprehensive and profound analysis of paladares.
10 ONEI, Anuario Estadístico de Cuba 2015.
11 ONEI, Anuario Estadístico de Cuba 2014 (La Habana, 2015).
12 Mesa-Lago et al., Voces de cambio en el sector no estatal cubano; ONEI, Anuario Estadístico de Cuba 2015.
13 Valdés notes in the prologue to Pérez Villanueva and Torres’s book the absence of a macroeconomic essay to place all NSS forms in the proper context.
14 The percentage of GDP generated only by self-employment has been estimated as 5 percent by Saira Pons, Tax Law Dilemmas for Self-Employed Workers (La Habana, CEEE), but by 12 percent by Torres (in Pérez Villanueva and Torres, p. 24), a significant gap. For an assessment of some NSS effects see Mesa-Lago et al., Voces de cambio en el sector no estatal cubano.
15 After this essay was finished, the guidelines (lineamientos) for 2016–2021 were published; a rapid browse indicates no significant changes from the guidelines of 2011.
16 Raúl Castro Ruz, “Informe central al Séptimo Congreso del Partido Comunista de Cuba,” Granma, April 17, 2016 (emphasis added), 1–3. Mauricio Murillo mentioned, as examples of the limits to be imposed, the establishment of limits on the number of hectares that somebody may have (“Intervención en el VII Período Ordinario de la Asamblea Nacional,” Granma, July 9, 2016).
17 Carmelo Mesa-Lago, “El lento avance de la reforma en Cuba,” Política Exterior 30, no. 171 (2016): 94–104.155
Presented at Florida International University, Cuban Research Institute Conference: “Beyond Perpetual Antagonism: Re-imagining U.S. – Cuba Relations.”
February 24, 2017
By Arch Ritter
How Carleton profs brought Western economics to Cuba
 Justin Trudeau speaks to a University of Havana audience plus officials in the Aula Magna, Universidad de la Habana, November 16, 2016
Justin Trudeau speaks to a University of Havana audience plus officials in the Aula Magna, Universidad de la Habana, November 16, 2016
Here’s how it happened: after the Soviets ended their “special relationship” with Cuba, the faculty of economics at the University of Havana wanted to introduce supply-demand micro and macroeconomics into its curriculum.
This was no small problem. Soviet economics had virtually disappeared, and Cuban economists were left orphaned. They didn’t even speak the language of Western economics, and they found it difficult to communicate with their counterparts in the rest of the world.
Carleton economist Archibald “Arch” Ritter, an expert in economic development, was at the first meeting in Havana in December 1993. The meeting brought together academics from Canada, Chile, Argentina and the University of Havana as well as officials from the International Development Research Centre (IDRC) to hammer out a plan.
The group decided to organize a joint master’s program in economics, mainly for young faculty members from Cuban universities, to be offered at the University of Havana. Carleton’s then-president Robin Farquhar approved the agreement. The program was up and running six months later.
Financed for the first two years by the IDRC and in its final three years by the Canadian International Development Agency with support from the United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America, the program was later expanded to include biology, business, linguistics, women’s studies and public administration. Professors were recruited from Canada and Latin American countries.
“It was neat to jump-start the introduction of Western economics to Cuba,” says Ritter, who taught in Havana part-time for five years. “And we did it on a shoestring budget.”
The project had broad support at the University of Havana, but it was far from unanimous, says Ritter. The students, however, “were all most congenial and very keen.”
In his blog, former student Luis Casaco, who now lives in Uruguay, recalls the day a stranger arrived in a classroom while he was making a presentation. She identified herself as a member of the communist party. The presentation continued, but there was a confrontation and the students defended their position that Cuba needed a radical transformation towards a market economy and a democratic system.
The woman angrily left the classroom. The next day, Casaco was called in for an urgent meeting.
“The woman started speaking in an irritating, slowly and softly way on the importance of the program, while emphasized the interest of some sectors in the university to dismantle it,” Casaco recalled. “She started to get angry, and said that the university belongs for the revolutionary people.”
Casaco’s professors came to his aid, including Ritter. “If they threaten you and intend to force you to stop free-speaking, I will shut down this program,” he recalls Ritter saying. “And then he added: ‘This is not a class of the communist Cuban party; this is a Carleton University class.’”
The program ran until 2001. Between 1991 and 1997, there was a shortage of food in Cuba after subsidies from the Soviet Union ended. “People were very thin,” said Ritter.
Many of the Cuban graduates went on to earn PhDs in economics both inside Cuba and at Carleton. Some left Cuba and built their lives elsewhere. According to Ritter’s count, 31 of the 76 graduates had left Cuba to go to Canada, the U.S. and countries in Latin America as of 2010.
“We contributed to a change in the climate of opinion, and changed the teaching of economics,” says Ritter.
 Carleton University economics professor Arch Ritter, pictured in Cuba in 2015 in a 1955 Chevrolet, taught part-time for five years at the University of Havana.
Carleton University economics professor Arch Ritter, pictured in Cuba in 2015 in a 1955 Chevrolet, taught part-time for five years at the University of Havana.
Ritter is often called upon to answer questions about Cuba. So, what will happen in the wake of Fidel Castro’s death?
Ritter doesn’t think it will change much. Castro has been mostly out of the picture since he became ill about a decade ago. Castro’s brother Raúl, now 85, served under his brother for 46 years. He was officially made president in 2008, and instituted a major set of reforms in 2010-11, which have liberalized small businesses.
“I don’t see much of change in the short run,” says Ritter. “Raúl will pretty much pick his successor. The succession will follow Raúl’s line. Raúl is very cautious. It took him almost five years to decide on the reform package.”
By Arch Ritter October 5, 2016
Canada and Cuba have maintained a normal and mutually beneficial economic relationship from Colonial times to 2016. With the beginning of Cuba’s “Special Period” in 1990 and its modest moves towards a mixed market economy in the 1990s, Canadian participants were optimistic about future economic relations. In the 2000’s, this was replaced by some skepticism, but with the reforms of 2010-2012 and the beginning of the normalization of US Cuba relations, optimism has returned. This article provides an update on Cuban-Canadian economic relations, including trade, foreign investment, development assistance and migration and some speculation concerning the future of the relationship.
Canada-Cuba Trade Relations
Since the start of Cuba’s revolution, normal trade relations between Canada and Cuba have been maintained. However, trade has waxed and waned over the years as can be seen in Chart 1. The chief feature of the trade relationship in the 1980s was the large volume of Canadian exports which were mainly wheat. Trade expanded steadily in the 1990s with the ending of the special trade relationship with the Soviet Union, as Cuba’s economy began to recover and as it began to diversify its export markets and sources of imports.
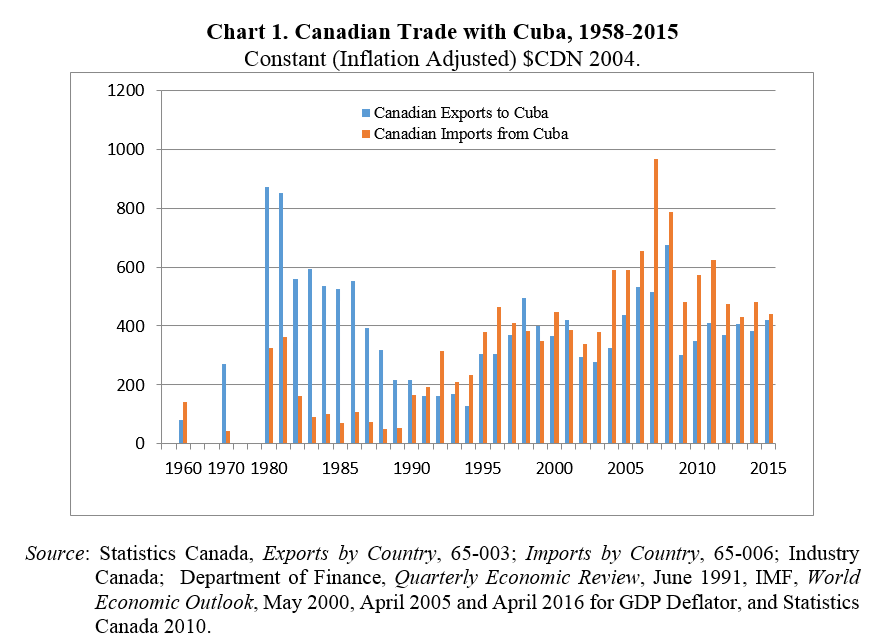 After 2001, Cuba’s exports to Canada expanded and began to exceed Canada’s exports to Cuba due to high nickel volumes and prices. Canadian exports to Cuba have more or less stagnated since 2001 while other countries have increased their market shares. By 2015, Canada was the fourth ranking exporter to Cuba following Venezuela, China, and Spain (Table 1.) In contrast, Canada was the second largest export market for Cuba after Venezuela in 2015, accounting for 11% of Cuba’s exports.
After 2001, Cuba’s exports to Canada expanded and began to exceed Canada’s exports to Cuba due to high nickel volumes and prices. Canadian exports to Cuba have more or less stagnated since 2001 while other countries have increased their market shares. By 2015, Canada was the fourth ranking exporter to Cuba following Venezuela, China, and Spain (Table 1.) In contrast, Canada was the second largest export market for Cuba after Venezuela in 2015, accounting for 11% of Cuba’s exports.
Cuba’s exports to Canada have consisted almost totally of nickel concentrates, with cigars, rum, seafood and copper scrap (presumably a quirk in 2015) as very small foreign exchange earners (Table 2.).
By 2015, Canada’s exports to Cuba were reasonably diversified (Table 2.) Its agricultural exports remained significant, though overwhelmed by US agricultural exports. Minerals (sulfur for Cuba’s nickel industry, potash for fertilizer), metals (copper products for Cuba’s electrical system mainly) and machinery of various types have all been significant in the 2010s.
Cuba’s best and most faithful friend is the brutal Canadian Winter, which has driven millions of Canadians to warmer Caribbean climes during the December to April period. Canada has been the largest single national source of tourists consistently from 1990 to 2015 and accounted for almost 40% of all tourist arrivals in 2015. But when US tourism opens up completely, there will likely be a deluge of US winter-escape tourism as well as curiosity tourism, convention tourism, medical tourism, March-break tourism and retirement relocation. The result will likely be that prices rise, and Canadian winter time tourism may well be squeezed out of Cuba into lower cost destinations.
 Canadian Enterprises in Cuban Joint Ventures
Canadian Enterprises in Cuban Joint Ventures
In 1991, Cuba opened itself to foreign investment in joint venture arrangements with state firms. By the end of 1999, there were 72 joint ventures or “economic association” agreements between Canadian firms and Cuban state enterprises but few seem to have ever come to life.
Sherritt International has been by far the most successful Canadian-Cuban joint venture. Its formula for success is one that cannot likely be replicated by any other enterprise. In effect, it exchanged 50% of its ownership in the nickel refinery in Alberta Canada for 50% ownership of the Moa mine and concentrator in Cuba and shared in the ownership of the marketing enterprise. This made Cuba a significant foreign investor in Canada! The Sherritt experience was explored in the previous issue of this publication.
A number of mineral exploration companies established joint ventures in Cuba by 1994 in association with Geominera S.A. It was thought that Cuba was an ideal location for mineral exploration because much of the country had been covered by aero-magnetic and geological surveys in the Soviet era. Among the enterprises involved in exploration projects in joint ventures with Geominera were Holmer Gold Mines, Joutel Resources, CaribGold Resources, Northern Orion, and MacDonald Mines. Unfortunately, the exploration undertaken from 1992 to 2007 yielded disappointing results and none of the exploration projects led to producing mines. This suggests that either the quality and/or magnitude of the deposits are lower than in other regions of the world. Alternatively, perhaps the investment conditions, the policy environment and/or the political risk situation were worse than elsewhere. It would be surprising if there were another mineral exploration rush in the medium term future, unless mineral prices were to rise to very high levels.
Canadian enterprises in real estate development have also had difficult experiences in Cuba. One project announced in October 1998 by an association between Cuba’s luxury hotel chain, Gran Caribe and Cuban Canadian Resorts International proposed U.S. $250 million set of four condominiums with hotel and resort facilities. It would have opened up an important new type of tourism for Cuba. However, in May 2000, the Ministry of Foreign Investment and Cooperation announced a prohibition of foreign ownership of condominium units killing this and other such projects for the time being.
Another project was that of Leisure Canada for the construction of some 11 hotels and two golf courses, a marina. (Leisure Canada Incorporated, 2000). This project fizzled out. In 2011 Leisure Canada, having changed its name to 360 VOX Corporation, was bought out by Dundee Corporation in May 2014. Any mention of this project has disappeared.
One successful venture was the construction of five airports in Cuba, including Varadero and Havana International Airports by Intelcan Technosystems of Ottawa. The CDN$ 52 million investment in the Havana Airport, was financed in part by Canada’s Export Development Corporation (33%) and 15% from Intelcan. Since 2000, the ultimate payment has come from international passengers who pay U.S. $25.00 (CUC 25.00) as an airport tax on departure.
Unfortunately brilliant successes for Canadian-Cuban joint ventures seem to be few and far between. Indeed, a number of executives of Canadian trading enterprises and joint ventures, Cy Tokmakjian and Sarkis Yacoubian, were jailed and tried on corruption charges –a cooling factor in the foreign investment process. The moral of the story is that establishing a joint venture in Cuba can work, but it must be done with patience, intelligence, and scrupulous awareness of Cuban regulations and processes and with clear benefits for the Cuban partner enterprise and the Cuban people.
Canadian Development Assistance
The Canadian International Development Agency (CIDA) has provided some interesting development assistance to Cuba since 1994. A major proportion of this has been “economic” in character, aimed at the “modernization of the state.” Some has been used to support the initiation of projects by Canadian enterprises with Cuban counterparts or to promote Canadian exports. Some of the economic programs were micro-enterprise tax administration, economic management, support for technical training and computer acquisition at the Central Bank, a program to help strengthen administration and professional economics at the Ministry of Economics and Planning and training/certification programs for tradesmen in some basic industrial areas. Various types of commodity assistance were provided as well. Much of the assistance provided by NGOs was aimed at community level activities. A small amount of assistance was directed towards human rights and governance initiatives including a “Human Rights Fund Pilot Project” and “Dialogue Fund” with multiple Canadian and Cuban partners.
 Canada’s active development assistance projects in Cuba as of mid-2016 are listed in Table 3. The annual expenditures of these multi-year projects for 2014-2015 was $CDN 2.42 million, a very
Canada’s active development assistance projects in Cuba as of mid-2016 are listed in Table 3. The annual expenditures of these multi-year projects for 2014-2015 was $CDN 2.42 million, a very
International Migration
An interesting dimension of Canadian-Cuban relations is migration. As indicated in Chart 3, Cuban migration to Canada has risen from levels in the hundreds in the 1980s to around 1,400 in 2014-2015. However, an unknown number of the Cuban immigrants to Canada move on to the United States, especially Florida, reflecting the attraction of the large Cuban-American population there and the weather.
Detailed sociological information on Cuban migrants is not available. However, my impressions are that, generally speaking, they are relatively well-educated, industrious, self-activating and entrepreneurial. They also seem to be relatively young, for the most part, many having recently finished their education and just starting out on their careers. Many Cuban immigrants seem to have done reasonably well and have found work in their professional areas, something that is not easy in a new society, culture and language. This migration represents a “brain drain” or a loss of human capital for Cuba and a corresponding gain for Canada.
Prospective Canadian-Cuban Economic Relations
The future economic relationship between Canada and Cuba will be shaped mainly by three factors: the strength and durability of Cuba’s economic recovery; the nature of Cuba’s economic policies affecting trade, and foreign investment; and the character and timing of complete normalization of relations with the United States.
A sustained recovery of the Cuban economy would promote a deepened and broadened economic relationship with Canada. A growing Cuban economy would permit increases in imports from all trading partners, including Canada. At the same time, economic recovery in Cuba also requires expansion of its exports of goods and services.
Is an enduring recuperation of the Cuban economy probable in the next decade or so? First, the driving force for the Cuban economy, namely export earnings, at this time depends mainly on tourism, medical services and nickel exports. Nickel and tourism should continue to be strong, but the obscured subsidization from Venezuela is over. Cuba’s medical service exports will likely be transitory as other countries develop their own medical systems and increase medical personnel. Pharmaceutical exports may hold promise in the longer term but have been somewhat disappointing relative to the high hopes once placed in their prospects. Little progress appears imminent regarding the expansion of other merchandise exports. New exports of manufactured products have not appeared on the scene in a significant way and are obstructed by some public policies.
Some continuing problems may prompt skepticism regarding Cuba’s economic prospects in the near future. Among the difficulties often cited are: a dual exchange rate system with negative consequences for export diversification and expansion; a blockage of people’s initiatives, energies and entrepreneurship due to the unwillingness to extend further the reform process especially for medium scale enterprise; and the deterioration of parts of the infrastructure, most notably housing.
The second set of factors that will shape Canada’s future economic relations with Cuba in is Cuba’s policies relating to trade, foreign investment and tourism. These policies are unlikely to undergo dramatic change under Raul Castro’s leadership. This implies that the basic Canadian-Cuban economic relationship should not be affected seriously by changed Cuban policies in the next few years. The state-trading that in part characterizes these relationships is not intrinsically beneficial for Canada.
Thirdly, the complete normalization of U.S. – Cuban relations especially regarding trade and US investment in Cuba, will have a major effect on the Canada-Cuba economic relationship. Complete normalization will permit expansion of Cuban exports, US foreign investment in Cuba, US tourism in Cuba, financial flows and the possibility of open and vigorous collaboration of Cuban-America and Cuban citizens in business activities. Greater prosperity will be the result.
Normalization with the United States will lead to expanded exports of goods and services to Cuba from the U.S. and vice versa. This is due to geographic and transport factors. More frequent freighter connections, high speed hydrofoil passenger boat connections, a re-connection of U.S. and Cuban railway systems and a proliferation of airline connections will lead to a reintegration of the two economies. The diversified U.S. economy can provide a broad range of consumer and capital goods and services competitively with other countries and with low transport costs and quick delivery times.
Canadian exporters to Cuba therefore will face a challenge after US – Cuban normalization. The location and logistical advantages of U.S. exporters, plus the interest, activism and advantages of the Cuban-American business community will outweigh any lingering “goodwill effect” with Canada. Overnight or next-day delivery of products ordered from the U.S. makes continuation of some types of exports from Canada difficult, as delivery from Canada currently may take up to two weeks or more on ships leaving Canada every week or ten days on average.
On the other hand, some of Canada’s current exports to Cuba are competitive with U.S. products and should increase in a post-embargo Cuban economic recovery. This might include fertilizers (potash), cereals, animal feed stocks, lumber, wood and paper products and fabricated non-ferrous metals products. Canada also is competitive in certain types of capital equipment such as minerals machinery and equipment, some paper making equipment, Bombardier aircraft, railway rolling stock and equipment, urban transit vehicles, communications equipment, electrical generation and distribution equipment, and some specialized vehicles. However, some Canadian exports may be threatened by U.S. competition.
In summary, the recovery of the Cuban economy and the increase in foreign exchange receipts that U.S.-Cuban normalization in time should bring about will be of benefit for some Canadian exporters while others may be replaced by U.S. suppliers. Will the “expansionary effect” outweigh the costs of the “displacement effect” for Canadian exporters? Perhaps, but this is not assured.
Normalization will also induce U.S. enterprises to invest in Cuba. With no further changes to the foreign investment law and within the current policy environment, one can imagine some but not many U.S. firms entering joint ventures. But with policy liberalization in a post-Raul Castro situation, one can imagine large numbers of U.S. enterprises investing in Cuba. Cuban-Americans would also enter Cuba to set up small businesses or to finance business ventures with their Cuban relatives or counterparts. The “geo-economic” gravitational pull of the U.S. will be strong. After U.S.-Cuba rapprochement Canadian trade and investment as a proportion of total trade and investment will likely diminish even though both might increase in absolute terms.
To conclude, there are future uncertainties and challenges regarding the Canadian-Cuban economic relationship. The character and intensity of future economic performance in Cuba, Cuba’s policy environment and the timing of the complete normalization of relations with the United States are still ambiguous and uncertain. These factors will have mixed effects, but effects that on balance should be positive for Canada and Cuba.
Bibliography
Citizenship and Immigration Canada. http://www.cic.gc.ca/english/resources/statistics/facts2014/permanent/10.asp. Accessed October 23, 2016
Cuban Club Resorts. 2000. Web site: www.cubanclubresorts.com
Global Affairs Canada, Cuba – International Development Projects, http://www.acdi-cida.gc.ca/cidaweb/cpo.nsf/fWebCSAZEn?ReadForm&idx=00&CC=CU. Accessed 3 October 2016
Industry Canada, Trade Data Online (TDO), Trade by Product (HS Codes) http://www.ic.gc.ca/eic/site/tdo-dcd.nsf/eng/Home
Leisure Canada Incorporated. (2000, August, 17). Press Release. Reproduced in www.cubanet.org
Nolen, Stephanie. 2015. In tourist-deluged Cuba, Canadian firms are noticeably absent. The Globe and Mail December 13.
Oficina Nacional de Estadisticas, Cuba. Anuario Estadistico de Cuba. (Various issues) http://www.one.cu/ . Accessed various times and October 4 2016.
Sequin Rob. 2013. Leisure Canada now a defunct Cuba real estate development brand. Havana Journal September 25,